|
Imidazole
is a heterocyclic compound of five-membered diunsaturated ring structure
composed of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms at nonadjacent positions.
The simplest member of the imidazole family is imidazole itself, colorless to
pale yellow crystalline solid with a weak aminelike odor; soluble in water and
alcohol, melts at 89 C, boils at 256 C. Imidazoles are poorly soluble in water
generally, but are dissolved in organic solvents, such as chloroform, propylene
glycol, and polyethoxylated castor oil. Imidazole ring is found in histidine (an
essential amino acid) and histamine, the decarboxylated compound from histamine.
Some imidazole compounds inhibit the biosynthesis of ergosterol, required in
cell membrane in fungal. They have antibacterial, antifungal, antiprotozoal, and
anthelmintic activity. Several distinct phenylimidazoles are therapeutically
useful antifungal agents against either superficial or systemic infections.
Thiabendazoles which have anthelmintic and antifungal properties are imidazole
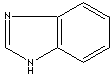
class compounds. Benzimidazole is a dicyclic compound having midazole ring fused
to benzene. Benzimidazole structure is a part of the nucleotide portion of
vitamin B12 and the nucleus in
some drugs such as proton pump inhibitors and anthelmintic agents. Imidazole has
two nitrogen atoms. The one is slightly acidic, while the other is basic.
Imidazole and its derivatives are widely used as intermediates in synthesis of
organic target compounds including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, dyes,
photographic chemicals, corrosion inhibitors, epoxy curing agents, adhesives and
plastic modifiers. Some imidazole analogues which contain nitrogen in
five-membered ring structure are:
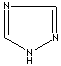
- Triazole: An
analog of imidazole.It has three nitrogen atoms and two carbon atoms at
nonadjacent positions in the ring system.
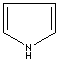
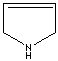
- Pyrrole: An
analog of imidazole. It has only one nitrogen atom in the ring system. Pyrrole
ring system is involved in coloured products (green pigment, chlorophyll; red,
hemoglobin; , blue, indigo) in nature.
- Pyrroline: A
pyrrole in which one of the two double bonds are hydrogenated.
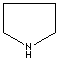
- Pyrrolidine:
The saturated tetrahydropyrrole, a part of the structures of amino acids
(proline, hydroxyproline and hygrine).
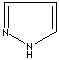
- Pyrazole:
1,2-Diazole (Imidazole isomer). The nitrogen positions are 1 and 2. It is not
found in nature
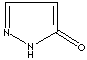
- Pyrazolone:
Pyrazole analog with ketone group at 5 positon
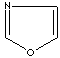
- Oxazole: an
analog of imidazole. The nitrogen atom in position 1 is replaced by oxygen.
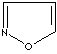
- Isoxazole:
an analog of pyrazole. The nitrogen atom at position 1 is replaced by
oxygen.
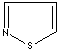
- Isothiazole:an analog of pyrazole. The nitrogen atom
at position 1 is replaced by sulfur.
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,2,4-Triazole |
Pyrrole |
1-Pyrroline |
3-Pyrroline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pyrrolidine |
Pyrazole |
Pyrazolone |
Oxazole |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isoxazole |
Isothiazole |
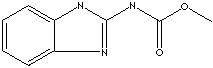
Benzimidazole |
Thiabendazole | Benzimidazole is
a white to slightly beige solid; melting at 172 C, boils at 360 C, slightly
soluble in water, soluble in ethanol. It is a dicyclic compound having imidazole
ring (containing two nitrogen atoms at nonadjacent
positions) fused to benzene. Benzimidazole and its
derivatives are used in organic synthesis and vermicides or fungicides as they
inhibit the action of certain microorganisms. Examples of benzimidazole class
fungicides include benomyl, carbendazim, chlorfenazole, cypendazole, debacarb,
fuberidazole, furophanate, mecarbinzid, rabenzazole, thiabendazole, thiophanate.
Benzimidazole structure is the nucleus in some drugs such as
proton pump inhibitors and anthelmintic
agents.
Benzimidazole class fungicides
include carbendazim, benomyl,
chlorfenazole, cypendazole, debacarb, fuberidazole,
furophanate, mecarbinzid, rabenzazole, thiabendazole,
thiophanate.
|