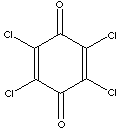
p-CHLORANIL
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
118-75-2
2914.70
2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-p-Benzoquinone; 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-1,4-Benzoquinone; 2,3,5,6-Tetrachloro-2,5-cyclohexadiene-1,4-dione; Tetrachloroquinone; 2,3,5,6-tetrachloro-p-Benzoquinone; 2,3,5,6-Tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone; Chloranile; Quinone Tetrachloride; Tetrachloro-p-benzoquinone; Tetrachloro-p-quinone; Tetrachlorobenzoquinone;
phenol with potassium chloride and hydrochloric acid
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Chloranil is used as a fungicide. It is used as an oxidizing agent in the organic synthesis especially for dye intermediates and vulcanization agent.
Benzoquinone is used as an oxidizing agent in organic synthesis. Some substituted benzoquinones are stronger reagents e.g o-chloranil, p-chloranilexist (tetrachlorobenzoquinone), and DDQ (2,3-dicyano-5,6-dichloro-parabenzoquinone). They are used as reagents for the oxidation (including oxidative coupling and cyclization reaction) and dehydrogenation of hydroaromatic compounds. They are useful in the synthesis of aromatized or lactones formed steroids and modified natural products. Metal dioxide such as selenium dioxide and manganese dioxide are also oxidising agents which convert alcohols into ketones, aromatic methyl groups into aldehyde or carboxylic acids, double bonds into alcohols, aldehydes into carboxylic acids, steroidal ketones into secolactones. But several side reactions are expected due to the lack of selectivity. DDQ and substituted quinones provide regioselective effectiveness for the preparation of target intermediates. Phenylbis(trifluoroacetato-O)iodine and Tritylium tetrafluoroborate are also reagent for the dehydrogenation of hydroaromatic compounds.|
Product |
CAS RN |
|
2,3-Dichloro-5,6-dicyano-p-benzoquinone |
84-58-2 |
| o-Chloranil |
2435-53-2 |
| Phenylbis(trifluoroacetato-O)iodine |
2712-78-9 |
|
p-Chloranil |
118-75-2 |
|
Tritylium tetrafluoroborate |
341-02-6 |
|
Selenium dioxide |
7446-08-4 |
|
Manganese dioxide |
1313-13-9 |
APPEARANCE
98.0% min
CHLORINE
56.5% min
0.5% max