PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
96-48-0
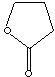
86.09
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
C1(=O)CCCO1
CLASSIFICATION
Solvent, Lactone, Tetrahydrofuran
EXTRA NOTES
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 3
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
206 C
3.0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
98 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - gamma-Butyrolactone
Wikipedia Linking - gamma-Butyrolactone
Google Scholar Search - gamma-Butyrolactone
U.S. National Library of Medicine - gamma-Butyrolactone
PubChem Compound Summary - gamma-Butyrolactone
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - gamma-Butyrolactone
ChEBI (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/) - gamma-Butyrolactone
NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/) - gamma-Butyrolactone
Material Safety Data Sheet - gamma-Butyrolactone
Human Metabolome Database - gamma-Butyrolactone
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - gamma-Butyrolactone
EPA - Substance Registry Services - gamma-Butyrolactone
Local:
Gamma-Butyrolactone is an intermediate for the manufacture of butyric acid compounds and pyrrolidones used as a plasticizer, solvent for polymers, nylon precursor and in insecticides. GBL is used as a solvent for surface treatment for textiles and metal coated plastics; polymers (ABS, PVC, polyvinylcarbazole, PS, nylons and cellulose acetate ); paint remover; petroleum industry for natural gas, acetylene, paraffins, and naphthene separations; viscosity modifier and curing agent for polyurethanes. GBL is also used in photochemical etching and vitamin and pharmaceutical preparations.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF LACTONE:
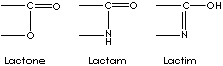
Lactone is an internal cyclic monoester (anhydride) derived from the hydroxyl and carboxyl radicals of gamma or delta hydroxy acids by the removal of a H2O between a carboxyl and a hydroxyl group in the same molecule; gamma-hydroxybutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactone and delta-hydroxydecanoic acid forms delta-decalactone spontaneously. In result, prefixes describe the ring size: beta- is for 4-membered ring), gamma- , 5-membered, and delta-, 6-membered ring. Lactam (a cyclic amide) is the nitrogen analog of lactone. Gamma-aminobutyric acid forms gamma-butyrolactam (also called 2-pyrrolidinone). Lactim is the tautomeric enol form of lactam. Lactam structure, a heteroatomic cyclic amide compound, is an important part in antibiotics such as penicillin. These structures, cyclic esters and analogues, are active nucleuses in pharmacological activity and flavorings. Their good solvency properties also useful in industrial application. Lactams have big demand in artificial fibre industry. They are polymerizable and used as nylon precursors.
APPEARANCE
99.5% min
COLOR, HAZEN
10 max
MOISTURE
0.2% max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Acute toxicity (Oral). Serious eye damage. Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure. Hazard statements: Harmful if swallowed. Causes serious eye damage. May cause drowsiness or dizziness.
GHS
Danger
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H302-H318-H336
P STATEMENTS
P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
22-41-67
SAFETY PHRASES
26-39