| CAS
NO. |
626-17-5 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
210-933-7 |
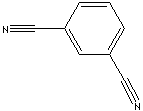
| FORMULA |
C6H4(CN)2 |
| MOL
WT. |
128.13 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral rat LD50: 860 mg/kg |
|
SYNONYMS |
1,3-Benzenedicarbonitrile; |
| 1,3-Dicyanobenzene; 1,3-Benzenedicarbonitrile; 1,3-Dicyanobenzene;
IPN; Isophthalonitrile; DCB; m-Dicyanobenzene; m-Benzenedinitrile;
3-Cyanobenzonitrile; m-PDN; Isoftalodinitril;
Nitril kyseliny isoftalove; 1,3-Benzodinitrile;
1,3-Benzendikarbonitril; Dinitrile of isophthalic acid; Isoftalonitril;
m-Cyanobenzonitrile; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to pale yellow powder |
| MELTING POINT |
161
C |
| BOILING
POINT |
265
C (sublimed)
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
0.992
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly
soluble |
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
soluble in benzene, ether, hot alcohol,
chloroform |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
| FLASH
POINT |
143
C
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
m-Phthalodinitrile
is an intermediate for the manufacture of
pesticide especially for Chlorothalonil.
It is also used in the production of synthetic fiber
and epoxy hardners. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white to pale yellow powder |
|
CONTENT
|
99.0%
min
|
|
Mononitrile |
0.5%
max
|
|
WATER
|
0.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kg in
bag |
| HAZARD CLASS |
6.1
(Packing Group: III) |
| UN
NO. |
2811 |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF PHTHALIC ACID |
|
Phthalic Acid, also called Benzenedicarboxylic Acid with formula C6H4(COOH)2, is
the name of any of three isomers. The ortho form (1,2-benzenecarboxylic acid)
is called simply phthalic acid. It is a white crystals decomposing at 191°C and
slightly soluble in water and ether. This compound is mainly produced and
marketed in the form of its anhydride produced by the oxidation of orthoxylene
and naphthalene. Its wide application is based on the ortho related carboxylic
acid groups as their dehydration is highly reactive with broad processing
conditions to produce various downstream products. It is used to make simple
esters widely used as plasticizers. It is used as in making unsaturated
polyester resins, alkyd resins, polyester polyols, dyes and pigments,
halogenated anhydrides, polyetherimide resins, isatoic anhydride and insect
repellents. The meta form is isophthalic acid (1,3-benzenecarboxylic acid). It
is a white crystals subliming at 345°C slightly soluble in water, alcohol and
acetic acid (insoluble in benzene). It is obtained by oxidizing meta-xylene with
chromic acid, or by fusing potassium meta-sulphobenzoate, or meta-brombenzoate
with potassium formate. IPA has excellent performance characteristics in coatings including excellent
hardness, corrosion and stain resistance, hydrolytic stability of coatings and
gel coats, excellent thermal stability and low resin color. It is a key ingredient in FRP markets for such products
as marine, automotive, and corrosion resistant pipes and tanks. Polyesters
containing isophthalic acid are also used extensively in industrial coatings
applications for home appliances, automobiles, aluminum siding, and metal office
furniture. It used as an intermediate for polyesters, polyurethane resins,
plasticizers. The para form, known as terephthalic acid (1,4-benzenecarboxylic
acid) is a combustible white powder insoluble in water, alcohol and ether;
(soluble in alkalies), sublimes at 300°C. It can be produced by oxidizing
caraway oil, a mixture of cymene and cuminol or by oxidizing para-diderivatives
of benzene with chromic acid. TPA has been used mainly as a raw material of
polyester fiber but lately it has been exploited for various uses such as
non-fiber field, PET-bottle, PET-film and engineering plastics and as poultry
feed additives. Phthalic acid derivatives are also widely used to make dyes,
medicine, and synthetic perfumes, pesticides, and other chemical compounds. |
|
Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-.
Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium
cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN
are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in
many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
|
