TRIDEMORPH
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
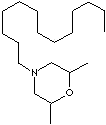
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
134 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
APPLICATIONS
Several morpholine derivatives, e.g., morpholinium salts of certain acylated sulfonamides, possess bactericidal activity. Morpholine hydroperiodide has been used as a water disinfectant (Texaco, 1986). Morpholine fungicides are used for agricultural purposes (Mercer, 1991), as foliar fungicides with protective and curative properties for the control of powdery mildew and rust (Brouwers et al., 1992; Leenheers et al. 1992), and as foliar fungicides for cereals (Ackermann et al., 1989). Morpholine is also used in the preparation of herbicides that can be applied either to the soil before the weeds emerge or to the growing plants (Texaco, 1986). (source: IPCS INCHEM)
Morpholine fungicides
|
Product |
CAS RN. |
|
Dodemorph |
1593-77-7 |
|
Benzamorf |
12068-08-5 |
|
Tridemorph |
24602-86-6; 81412-43-3 |
|
Carbamorph |
31848-11-0 |
|
Fenpropimorph |
67306-03-0 |
|
Aldimorph |
91315-15-0 |
|
Dimethomorph |
110488-70-5 |
|
Flumorph |
211867-47-9 |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min
MOISTURE
0.5% max