| INOSITOL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 87-89-8 |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 201-781-2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C6H12O6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 180.16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2906.13.1000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Inositol; Meat sugar; meso-Inositol; Dambose; Cyclohexanehexol; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hexahydrocyclohexane; 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexahydroxycyclohexane; Inosital; Inositene; Inositina; Insitolum; Mesoinosite; Mesoinositol; Phaseomannite; Phaseomannitol; i-Inositol; Other RN: 53319-35-0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
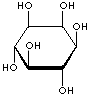
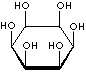
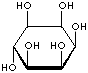
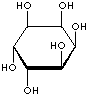
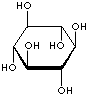
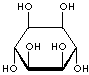
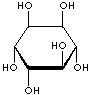
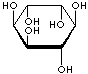
| SMILES | [C@@H]1([C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]([C@H]([C@H]1O)O)O)O)O)O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Vitamins / Inositol, Monosaccharide, Simple sugar |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTRA NOTES |
An isomer of glucose that has traditionally been considered to be a B vitamin
although it has an uncertain status as a vitamin and a deficiency syndrome has
not been identified in man. (From Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed,
p1379) Inositol phospholipids are important in signal transduction. A component of membrane phospholipids, glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchors that bind glycoproteins to cell membranes, and inositol phosphate second messengers. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Odorless White crystals | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 224 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | 14 gm/100 ml at 25C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Inositol PubChem Compound Summary - Inositol Drug Bank - Inositol KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Inositol http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Inositol http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Inositol Human Metabolome Database - Inositol http://naldc.nal.usda.gov/ Local: INOSITOL ISOMERS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
BIBLIOGRAPHY |
NF VII / FCC IV |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
White Crystals or Crystalline Powder | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IDENTIFICATION |
Pass Test |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
IRON |
5ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SULFATE |
60ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CALCIUM |
Complies |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HEAVY METALS |
5ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CHLORIDE |
50ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
0.5% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MELTING POINT |
224 - 227 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: n/a, Risk Phrases: n/a, Safety Phrases: 24/25-28A-37-45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||