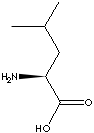
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
200-522-0
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white crystals
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture, light sensitive.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
APPEARANCE
white crystals
98.5 - 101.0%
SPECIFIC ROTATION
+14.5° ~ +16.5° (C=2 in 5N HCl)
LOSS ON DRYING
0.2% max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
CHLORIDE
0.02% max
SULFATE
0.03% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
IRON
10ppm max
ARSENIC
1ppm max
AMMONIUM SALTS
0.02% max
GENERAL PROPERTIES OF AMINO ACIDS
|
Amino Acid |
Abbreviation |
Formula (Mol WT) |
pK1 |
pK2 |
pKR |
pI |
Hydropathy Index |
|
|
3-Letters |
1-Letter |
-COOH |
-NH3+ |
R group |
||||
| Alanine |
Ala |
A |
C3H7NO2 (89.09) |
2.34 |
9.69 |
- |
6.00 |
1.8 |
| Arginine |
Arg |
R |
C6H14N4O2(174.20) |
2.17 |
9.04 |
12.48 |
10.76 |
-4.5 |
| Asparagine |
Asn |
N |
C4H8N2O3(132.12) |
2.02 |
8.80 |
- |
5.41 |
-3.5 |
| Aspartic Acid |
Asp |
D |
C4H7NO4(133.10) |
1.88 |
9.60 |
3.65 |
2.77 |
-3.5 |
| Cysteine |
Cys |
C |
C3H7NO2S(240.30) |
1.96 |
10.128 |
8.18 |
5.07 |
2.5 |
| Glutamic Acid |
Glu |
E |
C5H9NO4(147.13) |
2.19 |
9.67 |
4.25 |
3.22 |
-3.5 |
| Glutamine |
Gln |
Q |
C5H10N2O3(146.15) |
2.17 |
9.13 |
- |
5.65 |
-3.5 |
| Glycine |
Gly |
G |
C2H5O2(75.07) |
2.34 |
9.60 |
- |
5.97 |
-0.4 |
| Histidine |
His |
H |
C6H9N3O2(155.16) |
1.82 |
9.17 |
6.00 |
7.59 |
-3.2 |
| Isoleucine |
Ile |
I |
C6H13NO2(131.18) |
2.36 |
9.60 |
- |
6.02 |
4.5 |
| Leucine |
Leu |
L |
C6H13NO2(131.18) |
2.36 |
9.60 |
- |
5.98 |
3.8 |
| Lysine |
Lys |
K |
C6H14N2O2(146.19) |
2.18 |
8.95 |
10.53 |
9.74 |
-3.9 |
| Methionine |
Met |
M |
C5H11NO2S(149.21) |
2.28 |
9.21 |
- |
5.74 |
1.9 |
| Phenylalanine |
Phe |
F |
C9H11NO2(165.19) |
1.83 |
9.13 |
- |
5.48 |
2.8 |
| Proline |
Pro |
P |
C5H9NO2(115.13) |
1.99 |
10.60 |
- |
6.30 |
1.6 |
| Serine |
Ser |
S |
C3H7NO3(105.19) |
2.21 |
9.15 |
- |
5.58 |
-0.8 |
| Threonine |
Thr |
T |
C4H9NO3(119.12) |
2.09 |
9.10 |
- |
5.60 |
-0.7 |
| Tryptophan |
Trp |
W |
C11H10N2O2(204.23) |
2.83 |
9.39 |
- |
5.89 |
-0.9 |
| Tyrosine |
Tyr |
Y |
C9H11NO3(181.19) |
2.20 |
9.11 |
10.07 |
5.66 |
-1.3 |
| Valine |
Val |
V |
C5H11NO2(117.15) |
2.32 |
9.62 |
- |
5.96 |
4.2 |