|
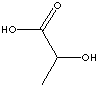
LACTIC ACID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO | 50-21-5, 79-33-4 (L), 10326-41-7 (D) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 200-018-0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | CH3CH(OH)COOH | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 90.08 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
2918.11.1000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral rat LD50: 3543 mg/kg | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | 2-Hydroxypropanoic acid; Lactic acid; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1-Hydroxyethanecarboxylic acid; Ethylidenelactic acid; alpha-Hydroxypropionic Acid; Milchsäure (Dutch); ácido lactico (Spanish); Aacide lactique (French); | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Acidum lacticum; Aethylidenmilchsaeure; DL-Lactic acid; Ethylidenelactic acid; Other RN: 152-36-3, 598-82-3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | C([C@@H](C)O)(O)=O | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Food acidity regulator, Preservative, Plant growth regulator |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTRA NOTES |
A normal intermediate in the fermentation (oxidation, metabolism) of sugar. The
concentrated form is used internally to prevent gastrointestinal fermentation. Conversion to glucose via gluconeogenesis in the liver and release back into the circulation FEMA No. 2611 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | Colorless to slightly yellow, syrupy liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 17 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT | 122 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | 1.209 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Miscible | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLVENT SOLUBILITY | Soluble in Alcohol, Furfurol, Glycerol | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| log P |
-0.72 (octanol-water) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2 Flammability: 1 Reactivity: 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FLASH POINT |
112 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Lactic acid PubChem Compound Summary - Lactic acid Drug Bank - Lactic acid KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Lactic acid http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Lactic acid http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Lactic acid Human Metabolome Database - Lactic acid Local:
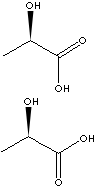
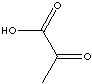
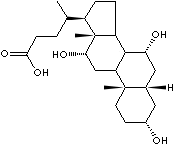
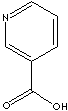
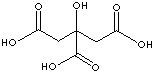
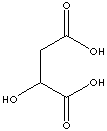
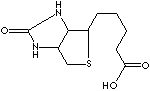
EXAMPLES
OF NATURALLY OCCURRING CARBOXYLIC ACIDS
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FCC IV 80 GRADE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| APPEARANCE |
Clear to slightly yellow liquid | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PURITY |
80% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CHLORIDE |
20ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SULFATE |
0.01% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.1% max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fe |
10ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
As |
1ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HEAVY METALS |
10ppm max |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | Not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SAFETY INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HAZARD OVERVIEW |
OSHA Hazards: Irritant |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
GHS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SIGNAL WORD |
Danger |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PICTOGRAMS |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
HAZARD STATEMENTS |
H315-H318-H338 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
P STATEMENTS |
P-261-P280-P302 + P352-P305 + P351 + P338 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EC DIRECTIVES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CODES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
RISK PHRASES |
37/38 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
SAFETY PHRASES |
41 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||