PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Phytic acid has an important function in the body as the inhibitor of the production of hydroxyl radicals and as the antioxidant to normalize cell. It is thought that this acts as a cancer fighter. It is believed it reduce blood clots and cholesterol and triglycerides which circulate through the blood-stream to prevent heart disease. It is also thought that IP6 enhances lymphocytes to kill tumor cells and prevents forming kidney stones. Furthermore, it has been reported that phytic acid inhibits the production of ammonia by binding to the iron molecule and has a deodorising effect on body odour, bad breath and uraroma. It is used as a complexing agent for removal of traces of heavy metal ions. It acts also as a hypocalcemic agent.
Phytic acid can prevent acute alcohol poisoning. Phytic Acid is used in food processing industry to reduce fermentation time and to prevent the change of properties or colors and oxidation in foods and wines due to its powerful chelating function. For industrial applications, it is widely used as the additive of metal coating and cleaning, as corrosion inhibitor for metal surface, desensitizers in ink, hard water treatment agent, gathering of rare earth and precious metals, antiknocking agent, antioxidant, preservative, and stabilizer.
Members of phytate
|
Product |
CAS RN |
| Phytic acid | 83-86-3 |
| Phytin | 3615-82-5 |
| Ferrous phytate | 3929-21-3 |
| Nonasodium phytate | 7205-52-9 |
| Calcium phytate | 7776-28-5 |
| Phytate 6-phosphatase | 9001-89-2 |
| Sodium phytate | 14306-25-3 |
| Dodecasodium phytate | 17211-15-3 |
| Monoferric phytate | 23567-85-3 |
| Phytate 3-phosphatase | 37288-11-2 |
| Phytate phosphatase | 37341-58-5 |
| Zinc phytate | 63903-51-5 |
| Copper phytate | 63903-50-4 |
| Hexasodium phytate | 70701-62-1 |
| Dodecapotassium phytate | 70981-46-3 |
| Plutonium phytate | 84926-55-6 |
| 90940-73-1 |
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
98.0% min
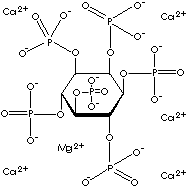
Ca
17.0% min
Mg
1.0 - 5.0%
ARSENIC
0.0003% max
SULFATE
0.02% max
CALCIUM
0.02% max
HEAVY METALS
0.003% max
CHLORIDE
0.02% max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF INOSITOL
Inositol ,chemically hexahydroxycylohexane, is any of nine stereoisomeric alcohols that closely resemble glucose in structure. It is a constituent of many cell phosphoglycerides. Meso- or myoinositol, named for its presence in muscle tissue, is biologically the important isomer. Myo-Inositol is the precursor in the phosphatidylinositol cycle, a source of two second messengers (diacylglycerol and inositol triphosphate). Inositols and their phosphates lack a hydrolytically labile glycosidic linkage and are stable to degradative enzymes in vivo. They have been used in the stable insulin mediators, inhibitors, and modulators. It is known that Inositols are effective in relieving symptoms of depression. Though inositols are not regarded as an essential nutrient in humans, they are sometimes classified as a member of the vitamin B complex (thiamine, riboflavin, niacin, pantothenic acid, biotin, pyridoxine, folic acid, inositol, and vitamin B12). Inositol is essential for the growth of some yeasts and fungi.
|
INOSITOL ISOMERS |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
cis-INOSITOL |
epi-INOSITOL |
allo-INOSITOL |
neo-INOSITOL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
myo-INOSITOL |
muco-INOSITOL |
scyllo-INOSITOL |
L-(-)-chiro-INOSITOL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
D-(+)-chiro-INOSITOL |
|
|
|