PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
6151-25-3 (Dihydrate)
204-187-1
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
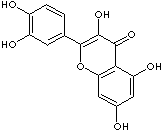
SMILES
c12c(oc(c3cc(c(O)cc3)O)c(c1=O)O)cc(O)cc2O
CLASSIFICATION
Flavonoid, Flavonol, Antioxidant
EXTRA NOTES
A flavonol widely distributed in plants. It is an antioxidant, like many other phenolic heterocyclic compounds. Glycosylated forms include RUTIN and quercetrin.
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 3
Other RN: 73123-10-1, 74893-81-5
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
8.1
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions. Moisture sensitive.
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Quercetin
Google Scholar Search - Quercetin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Quercetin
PubChem Compound Summary - Quercetin
Drug Bank - Quercetin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Quercetin
Chemical Entities of Biological Interest (ChEBI) - Quercetin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Quercetin
Human Metabolome Database - Quercetin
Material Safety Data Sheet - Quercetin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Quercetin
Local:
Quercetin, a common bioflavonol composed of two benzene rings linked with a heterocyclicpyrone ring (aromatic trimeric heterocyclic), is a water-soluble pigment synthesized or naturally occurring in the rind and bark of numerous plants. It, chemically 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7- trihydroxy- 4H-1-benzopyran-4-one, is a yellow to greenish crystalline powder melting at 302 C. Bioflavonoids are called phytochemicals, Vitamin P, and Vitamin C2. There are about 2000 known bioflavonoids including catechin, citrin, eriodictin, hesperetin, hesperidin, nobiletin, quercetin, rutin, sinensetin, and tangeretin. Vitamin P is not a dietary essential but is known to have the effect on capillary disorders. It increases the strength of the walls of the blood capillaries and regulates their permeability. It may have an contribution to the total antioxidant activity and detoxifiers. It may enhance the action of Vitamin C. It is considered that it lowers down cholesterol levels if it taken with Vitamin C. It is also know to have pharmacological action as an anti-inflammatory ,antihistaminic and antiviral agent.
|
|
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
96.0% - 102.0%
LOSS ON DRYING
9.0 - 11.0%
SULFATE
0.001% max
CHLORIDE
0.001% max
SULFATED ASH
0.2% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FLAVONOID
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin
PRICE INFORMATION