|
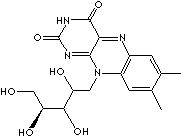
RIBOFLAVIN
| |||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
|||
| CAS NO. |
83-88-5 |
| |
| EINECS NO. | 201-507-1 | ||
| FORMULA | C17H20N4O6 | ||
| MOL WT. | 376.37 | ||
|
H.S. CODE |
2936.23.0000 | ||
|
TOXICITY |
Oral Rat LD50: > 10gm/kg | ||
| SYNONYMS | 7,8-Dimethyl-10-ribitylisoalloxazine; | ||
3,10-Dihydro-7,8-dimetyl-10-[(2S,3S,4R)-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl]
benzo[g]pteridine-2,4-dione; Ovoflavin; Zinvit-G;
Riboflavin; Lactoflavin; Vitamin B2;
6,7-Dimethyl-9-D-ribitylisoalloxazine, 7,8-Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)isoalloxazine;
7,8-Dimethyl-10-ribitylisoalloxazine; Aqua-Flave; Beflavin;
Beflavine; 7,8-Dimethyl-10-(D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)-
benzo(g) pteridine-2,4(3H,10H)-dione; 1-Deoxy-1-(3,4-dihydro-7,8-dimethyl-2,4-dioxobenzo(g)pteridin-
10(2H)-yl)-D-ribitol;
Dermadram; Fiboflavin; Flavaxin; Flavin BB; Flaxain; Hyflavin;
7,8-Dimethyl-10- (D-ribo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydroxypentyl)isoalloxazine;
7,8-Dimethyl-10-D-ribitylisoalloxazine; Lactobene; Lactoflavin;
Lactoflavine; Ribipca; Ribocrisina; Riboderm; Riboflavin; Riboflavina;
Riboflavine; Riboflavinequinone; Riboflavinum; Ribosyn; Ribotone;
Ribovel; Russupteridine Yellow III; Vitaflavine; Vitamin B2
; Vitamin Bi; Vitamin G; Vitasan B2; Other RN: 130609-39-1,
535950-32-4. 890044-91-4 |
|||
| SMILES | n1(c2c(nc3c1nc(=O)[nH]c3=O)cc(C)c(c2)C)C[C@H]([C@H] ([C@H](CO)O)O)O | ||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Natural Colorant, Vitamins, Dermatologic agent, Photosensitizing agent, Radiation-Sensitizing agent, Enzyme co-factor |
||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Nutritional factor found in milk, eggs, malted barley, liver, kidney, heart, and leafy vegetables. The richest natural source is yeast. It occurs in the free form only in the retina of the eye, in whey, and in urine; its principal forms in tissues and cells are as Flavin mononucleotide and Flavin-adenine dinucleotide. | ||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
|||
| PHYSICAL STATE | yellow to orange crystalline powder | ||
| MELTING POINT | 280 - 290 C (Decomposes) | ||
| BOILING POINT |
| ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Slightly soluble | ||
|
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY |
Soluble in dilute alkaline solutions, insoluble in alcohol | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| ||
| pKa | 10.2 (Dissociation Constant at 25 C) | ||
| log P | -1.46E+00 (Octanol-water) | ||
| VAPOR PRESSURE | 8.92E-22 (mmHg at 25 C) | ||
| HENRY LAW CONSTANT | 3.59E-19 (atm-m3/mole at 25 C) | ||
| OH RATE CONSTANT | 2.47E-10 (cm3/molecule-sec at 25 C Atmospheric) | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| ||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health hazard: 0, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 0 | ||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| ||
| FLASH POINT |
| ||
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions. Light sensitive. | ||
|
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION |
|||
|
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Riboflavin http://www.idpas.org/ http://www.eatright.org/
Consult a registered dietitian to find out how much of each vitamin is right for you. Remember, a variety of foods with plenty of vitamins and minerals is part of your ticket to good health. Local:
|
|||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | |||
|
BIBLIOGRAPHY |
USP23 / BP93 |
||
|
APPEARANCE |
yellow to orange crystalline powder | ||
|
IDENTIFICATION |
Complies (Test A, B) |
||
|
ASSAY |
98.0 ~102.0% | ||
|
OPTICAL ROTATION |
+56.5° ~ +59.5° |
||
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
1.5% max | ||
|
RESIDUE ON IGNITION |
0.2% max |
||
|
IMPURITY |
Complies |
||
| TRANSPORTATION | |||
| PACKING | 25kgs
in Fiber Drum | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | ||
| UN NO. | |||
|
PRICE INFORMATION |
|||