| CAS
NO. |
50-67-9 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
200-058-9 |
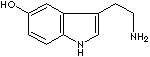
| FORMULA |
C10H12N2O |
| MOL
WT. |
176.22 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
3-(2-Aminoethyl) indol-5-ol; 5-HT; 5-Hydroxytryptamine;
Enteramine; |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to
off-white powder
|
| MELTING POINT |
167.5 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Slightly soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions. |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION
|
|
Serotonin, also called 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HTP), is an indole-containing
amino acid. In higher animals, it is found in high concentrations in many
tissues including in gastric mucous membranes, pineal body, central nervous
system and brain. Low levels are found in urine in the form of breakdown
products, 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA). It is also found in bacteria and
in many plants. Serotonin Serotonin is a biochemical messenger and regulator.
It is synthesized from L-tryptophan by hydroxylation and
decarboxylation. It is a monoamine vasoconstrictor, plays a role in brain and
nerve function and in stimulation of the smooth muscles, regulation of cyclic
body processes and pharmacologic actions. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white to
off-white powder
|
|
ASSAY |
98.0
- 101.0%
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
2.0%
max
|
|
RESIDUE
ON IGNITION
|
0.2%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
20ppm
max
|
|
ARSENIC
|
2ppm
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
Not
regulated |
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22,
Safety Phrases: 36 |
