PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
CLASSIFICATION
Alkene, Ichthyology, Triterpene
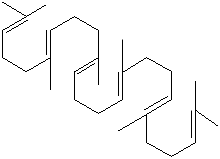
SMILES
A natural 30-carbon organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil (hence its name), although plant sources (primarily vegetable oils) are now used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
clear liquid
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - Squalene
Wikipedia Linking - Squalene
Google Scholar Search - Squalene
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Squalene
PubChem Compound Summary - Squalene
Drug Bank - Squalene
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Squalene
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Squalene
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Squalene
Material Safety Data Sheet - Squalene
EPA - Substance Registry Services - Squalene
Local:
Squalene is a triterpene found in human sebum and in large quantities in shark
liver oil. Terpene is a class of naturally occurring various unsaturated
hydrocarbons whose carbon skeletons are composed exclusively of five-carbon
isoprene unit. Isoprene units are assembled and modified in thousands of ways in
all living things, and are the largest group of natural products. Squalene plays
a role in the biosynthesis of sterols and polycyclic terpenes. It is used in
biochemical research, as a bactericide and as an intermediate in the synthesis
of pharmaceuticals.
APPEARANCE
clear liquid
IDENTITY
pass
ASSAY
98.0% min
PEROXIDE VALUE
5 max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF TERPENE
|
Class |
number of isoprene |
Examples |
|
Hemiterpene |
1 (C5H8) |
Found in associated with Alkaloids, Coumarins and Flavonoids. |
|
Monoterpenes |
2 (C10H16) |
Geraniol, Citronellol, Pinene, Nerol, Citral, Camphor, Menthol, Limonene, Thujone |
|
Sesquiterpenes |
3 (C15H24) |
Nerolidol, Farnesol |
|
Diterpenes |
4 (C20H32) |
Phytol, Vitamin A1 |
|
Triterpenes |
6 (C30H48) |
Squalene |
|
Tetraterpenes |
8 (C40H84) |
Carotene (Provitamin A1) |
|
Polyterpenes |
>10 (C5H8)n |
|