PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
SMILES
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
5.2
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
AUTOIGNITION
147 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Vanillic acid: the oxidation form of vanillin. The chemical designation is 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid.
Ethamivan: the diethylamide of vanillic acid; used as a central nervous system stimulant, respiratory stimulant, and analeptic.
Ethyl vanillin: white to pale yellow crystal; melting 76.5 C; having 3.5 times stronger flavour and more stable in organic solvents and in storage than vanillin but does not have the true flavour. It is used in pharmaceutical preparations and the food industry as a flavoring agent to replace or strengthen vanilla.
Acetovanillon: white crystal a faint vanilla odor; melting point 115 C; soluble in hot water, alcohol, benzene, chloroform, and ether; used as a cardiotonic drug. Chemical naming is 4'-Hydroxy-3'-methoxyacetophenone.
Wikipedia Linking:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Vanillin
http://www.chm.bris.ac.uk/
Is this it the same as Vanilla?:
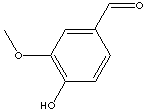
No. Vanillin is a single molecule, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde (much
easier to call it Vanillin), whose structure is shown in the image on the right.
It's a white crystalline solid, which melts at 81°C. Vanilla planifola is
an orchid which produces seed pods from which vanilla extracts are obtained;
these extracts contain nearly 200 different molecules, of which vanillin is the
most important, and most abundant, making up 98% of the eventual vanilla
extract. Vanillin itself was first isolated from vanilla pods by
Nicholas-Theodore Gobley in 1858 (though he thought that its formula was
C10H6O2, not
C8H8O2). The biosynthetic pathway starts with
phenylalanine.
http://valhalla.chem.udel.edu/
Synthesis of Vanillin:
Vanillin (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzaldehyde), a pleasant smelling aromatic
compound, occurs naturally in vanilla beans. It is used widely as a flavoring
additive for beverages, cooking, and as an aromatic additive for candles,
incense, potpourri, fragrances, perfumes, and air fresheners. It may be isolated
from the vanilla bean, and is often obtained as a byproduct of the pulp and
paper industry by the oxidative breakdown of lignin. It may also be prepared by
synthesis. We have developed (equation 1) a convenient two step synthesis of
vanillin using electrophilic aromatic substitution, followed by an
organometallic methoxylation procedure using copper bromide and sodium methoxide.....
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com
Vanillin
was one of seven phenolic compounds studied for their protective
properties against hydrogen peroxide-induced DNA damage in human
peripheral blood lymphocytes. Vanillin, curcumin, and resveratrol
protected against DNA damage induced by 50 ��M H2O2 at a concentration
range of 6.25 - 25 ��M....
APPEARANCE
PURITY (G.C.)
99.0% min
MELTING POINT
81 - 83 C
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max