| CAS
NO. |
59-02-9; 364-49-8;
18920-62-2; 121854-78-2 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
200-412-2 |
| FORMULA |
C29H50O2 |
| MOL
WT. |
430.17 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2936.28 |
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
D-alpha-Tocopherol;
(+)-alpha-Tocopherol;
|
| 3,4-Dihydro-2,5,7,8-tetramethyl-2-(4,8,12-trimethyltridecyl)-2H-1-
-benzopyran-6-ol; (2R,4'R,8'R)-alpha-Tocopherol; (R,R,R)-alpha-Tocopherol; (all-R)-alpha-Tocopherol;
2,5,7,8-Tetramethyl-2-(4',8',12'-trimethyltridecyl)-6-chromanol;
Mixed tocopherols; |
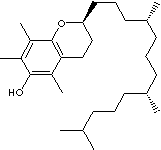
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
VITAMINS
/
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
Yellow
to Brown viscous liquid |
| MELTING POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble
|
|
SOLVENT
SOLUBILITY
|
Miscible with hydrocarbons, alcohols,
fats and oils
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
Tocopherol is a a fat-soluble vitamin. Vitamin E refers to a family of at
least eight molecules having a biological antioxidant activity and a structure
of chromanol ring substituted by an aliphatic side chain (C-12) containing two
methyl groups in the middle and two more at the terminal position. Chromanol
ring have a hydroxyl group which will reduce free radicals by the donation of a
hydrogen atom. The side chain is hydrophobic so that the molecules can penetrate
into biological membranes. Vitamin E exists in eight different forms or isomers,
four tocopherols and four tocotrienols. Tocopherol and tocotrienol are
distinguished by the saturatation of side chain; the side chain of four
tocopherols are saturated, whereas the four tocotrienols' side chains contain
three double-bonds, which are adjoined with a methyl group. The four tocopherols
and the four tocotrienols have an alpha, beta, gamma and delta form determined
by the number of methyl groups on the chromanol ring. The alpha form has three
methyl groups, the beta and gamma forms have two methyl groups and the delta
form has only one. Each form has its own biological activity. Alpha-tocopherol
is recognized as the most effective biological antioxidant. Tocotrienols have
more antioxidant potency than tocopherols, but human can digest tocotrienols
poorly and eliminates rapidly from the body. Tocotrienols are absorbed by the
skin and thus are used as an ingredient in a cream. Vitamin E is used in
as an moisturizing agent, an antioxidant
and to improve the elasticity of the skin in cosmetics and
skin care products, hair care and sun screening
products.
Members
of tocopherol
products
|
Product
|
CAS
RN
|
| D-gamma-Tocopherol
|
54-28-4 |
| D-alpha-tocopheryl acetate |
58-95-7 |
| Vitamin E
|
59-02-9 |
| Retinaldehyde
|
116-31-4 |
| delta-Tocopherol
|
119-13-1 |
| beta-Tocopherol
|
148-03-8 |
| beta-Tocotrienol |
490-23-3 |
| Methyltocols |
1406-66-2 |
| alpha-Tocotrienol |
1721-51-3 |
| alpha-Tocopherol dimer |
2896-55-1 |
| Tocopheronolactone
|
3121-68-4 |
|
D-alpha-Tocopherol succinate
|
4345-03-3
|
| gamma-Tocotrienol |
4382-43-8 |
| N-Methyl
alpha-tocopheramine |
4869-06-1 |
| Tocotrienol
|
6829-55-6 |
| Tocopherylquinone
|
7559-04-8 |
| beta-Tocopheramine
|
7591-11-9 |
| gamma-Tocopherol
|
7616-22-0 |
| alpha-Tocopheramine
|
7666-00-4 |
| Vitamin E acetate
|
7695-91-2 |
| alpha-Tocopherol dimer
|
7718-59-4 |
| Aescorin
|
8054-09-9 |
| alpha-Tocopheryl
polyethylene glycol succinate |
9002-96-4 |
|
DL-alpha-tocopherol
|
10191-41-0
|
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl calcium
succinate |
14464-85-8 |
| Tocopherol calcium succinate |
14638-18-7 |
| alpha-Tocopherol quinol
|
14745-36-9 |
| Vitamin E succinate
|
17407-37-3 |
| delta-Tocopheramine
|
18230-02-9 |
| Tocotrienol, delta
|
25612-59-3 |
| Tocophersolan |
30999-06-5 |
| Tocopheryl linoleate
|
36148-84-2 |
| alpha-Tocopherol
phosphate |
38976-17-9 |
| Tocopheryl retinoate
|
40516-49-2 |
| Tocopheryl nicotinate
|
43119-47-7 |
| 5-Nicotinooxymethyl-alpha-tocopherylnicotinate
|
51605-68-6 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopherol nicotinate |
51898-34-1 |
| Vitamin E acetate
DL-form |
52225-20-4 |
|
DL-alpha-Tocopherol phosphate disodium salt
|
60934-46-5
|
| 8-Hydroperoxytocopherone
|
67353-73-5 |
| Vitamin A, vitamin E
mixture |
70713-06-3 |
| N-Methyl-alpha-tocopheramine
nitroxide |
78249-60-2 |
| Chlorinated alpha-tocopherol |
80040-98-8 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-butylpicolinate |
85446-70-4 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(3,4-dibromobutyl)picolinate |
85446-72-6 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(3,4-dichlorobutyl)picolinate |
85446-73-7 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(4-bromobutyl)picolinate |
85446-74-8 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-benzylpicolinate |
85446-76-0 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-benzyloxypicolinate |
85446-77-1 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(4-chlorobutyloxy)picolinate |
85446-82-8 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(4-chlorophenyloxy)picolinate |
85446-83-9 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-butylthiopicolinate |
85446-84-0 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(3-chloropropylthio)picolinate |
85446-89-5 |
| DL-alpha-Tocopheryl 5-(2-propenyl)thiopicolinate |
85446-90-8 |
| N-4-Azido-2-nitrophenyl-beta-alanyl-gamma-tocopherol
|
99332-97-5 |
| Tocopheroxy radical
|
113085-06-6 |
| 8-((2,4-Dimethyl-1-nitrilopent-2-yl)dioxy)tocopherone
|
123438-35-7 |
| L-Ascorbic acid DL-alpha-tocopherol phosphoric diester potassium salt |
127061-56-7 |
| Epoxytocopherone
|
128442-18-2 |
| L-Ascorbic acid DL-alpha-tocopherol phosphoric diester sodium salt |
132746-07-7 |
| 1-Thio-alpha-tocopherol
|
133869-30-4 |
| 8a-Hydroperoxy-tocopherone
|
141913-27-1 |
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
BIBLIOGRAPHY
|
USP
/ FCC
|
|
APPEARANCE
|
Yellow
to Broun viscous liquid |
|
ASSAY
(VITAMIN E)
|
96.0
- 102% (per USP)
|
|
IDENTIFICATION
|
Passes
Test ( per USP)
|
|
ACID
VALUE
|
2.0
max ( KOH mg
/ g) |
|
ABSORPTIVITY
|
6
- 9 (255 nm) / 72-76 (292 nm) in Ethanol
|
|
SULPHATED
ASH
|
0.1%
max
|
|
HEAVY
METALS
|
10ppm
max
|
|
ARSENIC
|
3ppm
max
|
|
LEAD
|
10ppm
max
|
|
COPPER
AND ZINC
|
50ppm
max
|
|
VOLATILE
IMPURITIES
|
Passes
Test
|
|
FREE
TOCOPHEROL
|
1.0%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
190kgs
in Drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF ANTIOXIDANT
|
|
In industrial process, the term antioxidant refers to a chemical substance that
are added to prevent or delay deteriorations by the consumption of molecular
oxygen in the air, such as corrosion inhibition of metals, explosions, rubber
vulcanization, anti-knocking internal combustion, preservative of paints,
vegetable oils, and prepared foods. in biology, antioxidants act to protect
cells against free radicals. Free radicals play an important role in a number of
biological processes such as the intracellular killing of bacteria by neutrophil
granulocytes and certain cell signalling processes. However, because of their
reactivity, free radicals can cause side reactions resulting in cell damage,
which may contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Lipids, protein and nucleic acids are weak to free radicals. Free radicals may
be involved in the mechanisms of aging itself also. The body has a number of
mechanisms to minimize free radical induced damage and to repair damage.
Antioxidant enzymes produced in the body play a key role in these defense
mechanisms, such as glutathione peroxidase, glutathione reductase, catalase,
thioredoxin reductase and superoxide dismutase. Additionally, chemical
antioxidants neutralize free radicals by accepting or donating an electron to
eliminate the unpaired condition. These antioxidants include three vitamins
(vitamin A, vitamin C and vitamin E), polyphenols, bilirubin and uric acid.
Synthetic or natural antioxidants are widely used in nutrition and medicine and
prepared foods for the effect to slow down the natural aging process and to
prevent or delay certain diseases that result from cellular damage. But there
should be considerable researches whether antioxidant supplementation provide
beneficial effect, and if so, which and what amount of antioxidants are optimal.
There are hundreds of different types of nutritional antioxidants include
vitamins, coenzymes, selenium, minerals, hormones, carotenoids, non-carotenoid
terpenoids, flavonoids (flavonols, flavones isoflavones, flavanols,,
anthocyanidins), nonflavonoid phenolics, polyphenolics and their esters (ellagic
acids, citric acids, uric acids, gallic acids, salicylic acids, rosmarinic
acids, cinnamic acids, chlorogenic acids, chicoric acids) |
