PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
233-007-4
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
278 C
33.5
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://www.eurocdsoc.com/
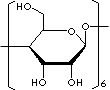
Cyclodextrins are a
group of structurally related natural products formed during bacterial digestion
of cellulose. These cyclic oligosaccharides consist of (α-1,4)-linked
α-D-glucopyranose units and contain a somewhat lipophilic central cavity and a
hydrophilic outer surface. Due to the chair conformation of the glucopyranose
units, the cyclodextrins are shaped like a truncated cone rather than perfect
cylinders. The hydroxyl functions are orientated to the cone exterior with the
primary hydroxyl groups of the sugar residues at the narrow edge of the cone and
the secondary hydroxyl groups at the wider edge. The central cavity is lined by
the skeletal carbons and ethereal oxygens of the glucose residues, which gives
it a lipophilic character. The polarity of the cavity has been estimated to be
similar to that of an aqueous ethanolic solution.
Local:
Cyclic structure oligomers of glucose ( called cyclodextrins) are obtained from
the starch digests of the bacteria Bacillus macerans. The individual glucose
units are connected by 1,4 bonds. The most abundant cyclodextrins are alpha,
beta and gamma cyclodextrin which have 6,7 and 8 glucose units respectively. The
interior cavity is hydrophobic and the outside of the molecule is hydrophilic.
The enhanced of characteristics such as stability, aqueous solubility, and
reduced volatility, can be modified through mainly propoxylation reactions of them.
Potential applications of cyclodextrins include water-soluble pharmaceuticals,
prolonged drug release, tabletting and herbicides and pesticides.
Some examples of commercially available cyclodextrin, or derivatives thereof, are as follows:
- alpha-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 10016-20-3)
- alpha-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-60-1)
- alpha-Cyclodextrin, sulfated Sodium salt Hydrate (CAS #: 699020-02-5)
- Hexakis (2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Hexakis (2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Hexakis(2,3,6-tri-O-octyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 140395-31-9)
- Hexakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 53784-82-0)
- Hexakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 131105-41-4)
- Hexakis (6-O-tertbutyl-dimethylsilyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Butyl-alpha-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-alpha-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-alpha-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-33-3)
- beta-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 7585-39-9)
- beta-Cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 68168-23-0)
- beta-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-61-2)
- beta-Cyclodextrin sulfate
- beta-Cyclodextrin, sulfated Sodium salt (CAS #: 37191-69-8)
- Hydroxypropyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 94035-02-6)
- 6-Monodeoxy-6-monoamino-beta-cyclodextrin
- 6-O-alpha-D-Glucosyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 92517-02-7)
- 6-O-alpha-Maltosyl-beta-cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 104723-60-6)
- Heptakis-6-azido-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis(2,3-di-O-acetyl-6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 196398-66-0)
- Heptakis-(2,3-di-O-methyl-6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 201346-23-8)
- Heptakis(2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 51166-71-3)
- Heptakis-(2,6-di-O-ethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 111689-03-3)
- Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 55216-11-0)
- Heptakis(2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis-(2,3,6-tri-O-benzoyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 23666-43-5)
- Heptakis-(2,3,6-tri-O-ethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 111689-01-1)
- Heptakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 30754-23-5)
- Heptakis-6-(dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl)-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-beta-cyclodextrin
- Monoacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Diacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Triacetyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 23739-88-0)
- Heptakis(3-O-acetyl-2,6-di-O-methyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 131889-29-7)
- Heptakis-(6-O-maltosyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Heptakis(6-O-sulfo)-beta-cyclodextrin Heptasodium salt (CAS #: 197587-31-8)
- Heptakis(6-O-t-butyldimethylsilyl-2,3-di-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-(2-hydroxypropyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2,6-Di-O-)ethyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2-Carboxyethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxyethyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-32-2)
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-35-5)
- Butyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Methyl-beta-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-36-6)
- Silyl((6-O-tert-butyldimethyl)-2,3,-di-O-acetyl)-beta-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- gamma-Cyclodextrin (CAS #: 17465-86-0)
- gamma-Cyclodextrin Hydrate (CAS #: 91464-90-3)
- gamma-Cyclodextrin phosphate Sodium salt (CAS #: 199684-62-3)
- Sulfopropyl-beta-cyclodextrin
- Carboxymethyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,3,6-tri-O-acetyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,3,6-tri-O-methyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis (2,6-di-O-pentyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis-6-(dimethyl-tert-butylsilyl)-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Octakis-6-bromo-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 53784-84-2)
- Octakis-6-iodo-6-deoxy-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 168296-33-1)
- Octakis (6-O-t-butyldimethylsilyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Succinyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- (2-Hydroxypropyl)-gamma-cyclodextrin (CAS #: 128446-34-4)
- Acetyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
- Butyl-gamma-cyclodextrin
PURITY
98.0% min
SPECIFIC ROTATION
MOISTURE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF DEXTRIN
PRICE INFORMATION