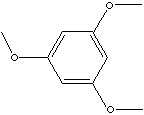
| 1,3,5-TRIMETHOXYBENZENE | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS NO. | 621-23-8 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS NO. | 210-673-4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FORMULA | C6H3(OCH3)3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MOL WT. | 168.19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
H.S. CODE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOXICITY |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SYNONYMS | Phloroglucinol trimethyl ether; Sym-Trimethoxybenzene; | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| O,O,O-1,3,5-trimethylresorcinol; O,O,O-1,3,5-Trimethylresorcin (German); O,O,O-1,3,5-Trimetilresorcinol (Spanish); O,O,O-1,3,5-Triméthylresorcinol (French); | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT | 51 - 53 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BOILING POINT |
255 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| pH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
FLASH POINT |
112 C | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STABILITY | Stable under normal conditions, light and air sensitive | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPLICATIONS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
There are three isomeric compounds of trihydroxybenzene molecule structure,
which all have traditional names respectively. Their names are related with the
equivalent dihydroxybenzene compounds. The names of the three compounds indicate
which of the hydrogens on the benzene ring portion of the molecule have been
replaced by hydroxyl groups. The isomer of 1,2,3-trihydroxybenzene is called
pyrogallic acid (or pyrogallol). This compound is a poisonous acid, derived
from gallic acid, and used in the manufacturing colorants such as azo dyes and
photographic developers and externally as an antimicrobial to treat certain skin
diseases. Phloroglucin (or called phloroglucinol) is 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene
which presents as the genin of many glycosides, particulrally in the bark of
apple and other trees. It is used in as a reagent for pentoses, pentosans,
glycuronates, hydrochloric acid in gastric juice. It is an excellent bone
decalcifying agent and a floral preservative. It is used in the manufacture of
pharmaceuticals. The 1,2,4- isomer is hydroxyquinol (or called
hydroxyhydroquinone). Trihydroxybenzenes have three hydroxyl groups in one
benzene ring. They can derive numerous esters and salts. They are used as
chemical intermediate to synthesis target molecules of pharmaceuticals,
pesticides, stabilizer, antioxidant, colorants, perfumes, photoinitiators, and
other organic compounds. Methoxylated
phenol family compounds have
bacteriostatic and floral preservative properties. They
are used in
pharmaceuticals and
flavorings. They are used in formulating insect attractants,
analgesics, biocides and antiseptics. They are also used in manufacturing
stabilizers, antioxidants, and UV absorbers for plastics and
rubbers. An
example of target product from 1,3,5-Trimethoxybenzene
is buflomedil, a vasoactive agent
which improves the symptoms of impaired blood circulation.
Members of phloroglucinol molecules
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystal | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MELTING POINT |
51 - 53 C |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TRANSPORTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PACKING | 25kgs
in drum | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HAZARD CLASS | not regulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UN NO. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: 28A/37/45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||