| CAS
NO. |
35543-25-0 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
252-612-4 |
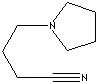
| FORMULA |
C8H14N2 |
| MOL
WT. |
138.21 |
| H.S.
CODE |
|
| TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
4-(N-pyrrolidino)butyronitrile;
|
| 1-Pyrrolidinebutanenitrile; 4-(1-Pyrrolidinyl)butanenitrile;
4-Pyrrolidinebutanenitrile; |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
clear
liquid |
| MELTING
POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
0.926 |
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health:
1; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 |
| FLASH
POINT |
99
C |
| STABILITY |
Stable
under normal temperatures and conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
| Pyrrole: One of a class of organic heterocyclic compounds of five-membered
diunsaturated ring structure composed of four carbon atoms and one nitrogen
atom. The simplest member of the pyrrole family is pyrrole itself, a basic
heterocyclic compound; colorless to pale yellow, toxic oil with pungent taste
and similar to chloroform odor; insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, ether,
and dilute acids; boils at 129 - 131 C; polymerizes in light. Pyrrole ring
system is involved in coloured products (green pigment, chlorophyll; red,
hemoglobin; , blue, indigo) in nature. Pyrrolidine, the saturated
tetrahydropyrrole, is part of the structures of amino acids (proline,
hydroxyproline and hygrine). Pyrroline is a pyrrole in which one of the two
double bonds has been hydrogenated. Pyrrole and its derivatives are widely used
as an intermediate in synthesis of pharmaceuticals, medicines,
agrochemicals, dyes, photographic chemicals, perfumes and other organic
compounds. They are also used as catalysts for polymerization process, corrosion inhibitors,
preservatives, and as solvents for resins and terpenes. They are used in
metallurgical processes. They are useful in the intensive study of transition-metal complex catalyst chemistry for uniform polymerization,
luminescence chemistry and spectrophotometric analysis.
1-Pyrrolidinebutanenitrile
is used to make pharmaceuticals
such as Buflomedil. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
clear
liquid |
| PURITY |
99.0%
min
|
|
WATER
|
0.5%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
180kgs
in drum |
| HAZARD
CLASS |
6.1
(Packing Group: III) |
| UN
NO. |
2810 |
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38,
Safety Phrases: 24/25 |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF NITRILE |
| Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C��N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC��N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ��N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC��N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+��C-.
Sodium cyanide, NaCN; potassium
cyanide, KCN; calcium cyanide, Ca(CN)2; and hydrocyanic (or prussic) acid, HCN
are examples. Chemically, the simple inorganic cyanides resemble chlorides in
many ways. Organic nitriles act as solvents and are reacted further for various application including;
·
Extraction solvent for fatty acids,
oils and unsaturated hydrocarbons
· Solvent for spinning and casting and
extractive distillation based on its selective miscibility with organic
compounds.
· Removing agent of colouring matters and aromatic
alcohols
· Non-aqueous solvent for titrations and for inorganic
salts
· Recrystallization of steroids
·
Parent compound for organic
synthesis
· Solvent or chemical intermediate in biochemistry ( pesticide
sequencing and DNA synthesis)
·
High-pressure liquid chromatographic
analysis
· Catalyst and component of transition-metal complex
catalysts
· Stabilizer for chlorinated
solvents
· Chemical intermediate and solvent for perfumes and
pharmaceuticals
|
