PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
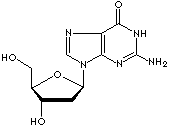
Guanosine: a purine nucleoside composed of guanine linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of ribose. It is a component of ribonucleic acid and its nucleotides (GMP, GDP, GTP, cGMP) play important roles in biochemical processes such as synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins, photosynthesis, muscle contraction and intracellular signal transduction (cGMP). GMP, GDP, GTP are three interconvertible compounds in which Guanosine is attached through its ribose group to one (monophosphate), two (diphosphate), and three (triphosphate) phosphoric acid molecules. Symbol G. Deoxyguanosine: a purine nucleoside, guanine linked by its N9 nitrogen to the C1 carbon of deoxyribose.
- Guanine:a pyrimidine base
- Guanosine Triphosphate (GTP) : a nucleotide composed of guanine, the sugar ribose, and three phosphate groups; the source of the guanosine found in RNA and also involved in many cellular processes, including microtubule assembly, protein synthesis, and cell signaling, due to the energy it releases upon removal of its terminal phosphate group (yielding GDP). The ratio of GTP to ATP is maintained by the reversible transfer of phosphate catalyzed by GDP kinase.
- Guanosine diphosphate (GDP) : a nucleotide composed of pyrophosphate of guanosine which serves as a carrier for mannose residues in glycoprotein synthesis and as a substrate for a phosphorylation reaction of the tricarboxylic acid cycle.
- Guanosine monophosphate (GMP, aso known as guanylic acid) : a nucleotide composed of pyrophosphate of guanosine which is formed during the hydrolysis of nucleic acidis and is a regulator of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis.
- Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP); 3',5'-cyclic ester of guanosine monophosphate that serves as an intracellular secondary involved its direct effects on Na+ and Ca2+ channels in the plasma membrane of rod cells. Its action is similar to that of cyclic adenosine monophosphate, but the two cyclic nucleotides activate different protein kinases and usually produce opposite effects on cell function. cGMP acts as an antagonist to cAMP.
- Deoxyguanosine diphosphate (dGDP) : a nucleotide, 5'-pyrophosphate of deoxyguanosine.
- Deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGMP) : a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyguanosine, occurring in deoxyribonucleic acid.
- Deoxyguanosine monophosphate (dGTP) : a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of deoxyguanosine; the source of the deoxyguanosine in DNA
Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism, the function of important enzymes, and cytobiology research.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
SULFATED ASH
0.5% max
WATER
7.0% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
Price: