| CAS
NO. |
88-82-4 |
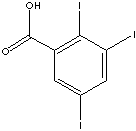
|
| EINECS
NO. |
201-859-6 |
| FORMULA |
C7H3I3O2 |
| MOL
WT. |
499.81 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
Oral rat LD50:
813 mg/kg |
| SYNONYMS |
TIBA; 2,3,5-Triiodbenzoesäure (German);
|
| ácido 2,3,5-triiodobenzoico (Spanish); Acide
2,3,5-triiodobenzoïque (French); |
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white
to off-white crystals |
| MELTING POINT |
220
- 223 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
Insoluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health: 1 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 |
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
FLASH
POINT
|
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under normal conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Iodine is a
nonmetallic halogen element in Group 17 of periodic table; atomic number 53;
atomic mass 126.9; melting point ca 114 C; boiling point ca 184 C; specific
gravity 4.93 g/cm3; Oxidation states: 7,5,1,-1; [Kr] 4d10 5s2 5p5. Iodine is a
nearly black poisonous, corrosive solid at room temperature and readily
sublimes to a deep violet vapour, the colour of which is responsible for its
name from Greek. It is insoluble in water, soluble in common solvents. Iodine is
required in small amounts in human body for the function of the thyroid gland.
Iodine forms many important compounds of iodine such as iodine(V)oxide,
potassium iodide, iodine trichloride and iodoform of an Iodine containing
organic compound. Iodine is used as a component in germicides and disinfectants
with surfactants to carry iodine. Potassium iodide is used as a heat stabilizer
and a catalyst in synthetic fiber manufacturing. Organic iodides
and Iodine
metal salts are used in formulating antiseptics and
x-ray contrast media compounds in pharmaceuticals. Potassium iodate and other
forms like calcium iodate and ethylene diamine dihydroiodide are used in animal
feeds to prevent deficiency of iodine. Iodine and its organic compounds are
useful in dye industry for
the high bright colors as well as pharmaceutical industry. An example of organic Iodine,
iodoform has weak bactericidal
qualities and is used to treat minor skin diseases. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to off-white crystals |
|
ASSAY
|
98.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
220
- 223 C |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 22, Safety Phrases: 24/25-28A-37-45 |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF BENZOIC ACID |
|
Benzoic acid, the simplest aromatic carboxylic acid containing carboxyl group
bonded directly to benzene ring, is a white, crystalline organic compound;
melting at 122 C (starting sublime at 100 C); boiling at 249 C; slightly
soluble in water, soluble in ethanol, very slightly soluble in benzene and
acetone. Its aqua solution is weakly acidic. It occurs naturally in many plants
and resins. Benzoic acid is also detected in animals. The most of commercial
benzoic acid is produced by the reaction of toluene with oxygen at
temperatures around 200 C in the liquid phase and in the presence of cobalt and
manganese salts as catalysts. It can be prepared also by the oxidation of
benzene with concentrated sulphuric acid or carbon dioxide in the presence of
catalysts. Other methods are such as by the oxidation of benzyl alcohol,
benzaldehyde, cinnamic acid; by hydrolysis of benzonitrile, benzoyl chloride.
More than 90% of commercial benzoic acid is converted directly to phenol and
caprolactam. Its use in the production of glycol benzoates for the application
of plasticizer in adhesive formulations is increasing. It is also used in the
manufacture of alkyd resins and drilling mud additive for crude oil recovery
applications. It is used as a rubber polymerization activators and retardants.
Benzoic acid is converted to its salts and esters for the use of preservative
application in foods, drugs and personal products. Sodium benzoate, sodium salt
of benzoic acid, is used preferably as one of the principal anti-microbial
preservatives used in foods and beverages (but it's concentration is limited
usually not exceeding 0.1% because it is poisonous), as it is about 200 times
more soluble than benzoic acid. Sodium Benzoate is also used in medications,
anti-fermentation additives and tabletting lubricant for pharmaceuticals. The
industrial applications are as a corrosion inhibitor, as an additive to
automotive engine antifreeze coolants and in other waterborne systems, as a
nucleating agents for polyolefin, as a dye intermediate, as a stabilizer in
photographic processing and as a catalyst. Wide range of benzoic esters are used
as solvents, dying carrier, disinfectant additive, penetrating agent and
pesticides and manufacturing other compounds. |
