| CAS NO. |
6631-94-3 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
229-626-4 |
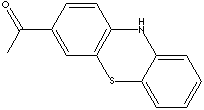
| FORMULA |
C14H11NO2 |
| MOL WT. |
241.31 |
|
H.S. CODE |
2934.30.4300 |
|
TOXICITY |
|
| SYNONYMS |
3-Acetylphenothiazine; -Acetylthiodiphenylamine; |
| Methyl phenothiazin-2-yl ketone; |
| SMILES |
S1c2ccccc2Nc2c1ccc(C(=O)C)c2 |
|
CLASSIFICATION |
Thiazine |
|
EXTRA NOTES |
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
| PHYSICAL STATE |
mustard-colored powder |
| MELTING POINT |
190 - 193 C |
| BOILING POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER |
Soluble |
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health:2; Flammability: ; Reactivity: |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
FLASH POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable under normal conditions |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
|
Phenothiazine, also called dibenzothiazine or thiodiphenylamine is a yellow or green crystalline compound soluble in hot acetic acid, benzene, and ether. It is a three-ring structure compound in which two benzene rings are joined by a sulfur and nitrogen atom at nonadjacent positions. It is obtained from by fusing diphenylamine with sulfur. Generally phenothiazine structure compounds are known as active adrenergic blocking agents. They are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing especially antipsychotic drugs. Phenothiazine and its derivatives are used in as worming agents (anthelmintic) in veterinary medicine effective against a wide range of parasitic insects in animals which provides food for human. (it is a highly toxic drug which is not recommended for human use directly). Phenothiazine is also used as a stabilizer against polymerization of acrylates. |
| SALES SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE |
mustard-colored powder |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min |
|
MELTING POINT |
190 - 193 C |
|
LOSS ON DRYING |
1.0% max |
|
ASH |
1.0% max |
|
PHENOTHIAZINE |
1.0% max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN NO. |
|
| OTHER INFORMATION |
|
Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 24/25 |
