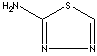
| 2-AMINO-1,3,4-THIADIAZOLE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 4005-51-0 |
|
| EINECS NO. |
223-657-7 | |
| FORMULA | C2H3N3S | |
| MOL WT. | 101.1258 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | 1,3,4-Thiadiazol-2-amine; 2-Amino-1-thia-3,4-diazole; ATDA; | |
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white crystalline powder | |
| MELTING POINT |
192 - 194 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
| |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
| |
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
| |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
| |
| FLASH POINT |
| |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Thiazole is a heterocyclic organic compound that has a five-member ring molecular structure, C3H3NS, containing three carbon atoms, one sulphur atom, and one nitrogen atom. It is a clear to yellowish liquid with a pyridine like odor. It is soluble in alcohol and ether and slightly soluble in water. It is parent material for numerous of chemical compounds including sulfur drugs, biocides, fungicides, dyes, chemical reaction accelerators. Thiazole dyes contain the color radicals of =C=N- and -S-C= which decide colors to a compound . Azo dyes contain -N=N- radical. Thiazole dyes are useful in dying cotton. Benzothiazole is a thiazole fused to benzene ring. Benzothiazole derivatives are important in the industry of dyes, photographic chemicals, sulfa drugs and rubber. Thiabendazole, a substituted derivative of benzimidazole, is used as broad-spectrum anthelmintic and presevative. Some thiazole derivatives, belong to a class of cyclic sulfur organo products containing sulfur atom (S) and often oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), hydrogen (H), as well as other elements, can find application for making biological activitive agents such as antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal , antituberculous, antbody and antifungal agents. Thiazole and its derivatives are also used as thiol flavouring substances. Thiadiazole contains the five-membered diunsaturated ring structure composed of two nitrogen atoms and one sulfur atom. Thiadiazole and its derivatives are used for biological activities such as antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal and antituberculous. Benzothiadiazole, fused to benzene ring with two nitrogen atoms at 1,3 position and one sulfur atom at 2 position in the five-membered ring, is known as an inducer of systemic resistance to diseases rather than direct antifungal or antibacterial activities. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white crystalline powder | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min |
|
| MELTING POINT |
192 - 194 C |
|
|
MOISTURE |
0.5% max |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 25kgs
in Drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | 2811 | |
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 22-40-63, Safety Phrases: 22-26-36/37 | ||