PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
200kgs in drum
|
|
|
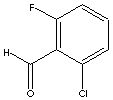
| 2-CHLORO-6-FLUOROBENZALDEHYDE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 387-45-1 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 206-860-5 | |
| FORMULA | ClC6H3(F)CHO | |
| MOL WT. | 158.56 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
|
|
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | 2-氯-6-氟苯甲醛; Benzaldehyde, 2-chloro-6-fluoro-; | |
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to yellow solid | |
| MELTING POINT | 35 - 38 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
| |
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 1; Reactivity: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | > 110 C | |
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions. Air sensitive | |
|
APPLICATIONS |
||
| Benzaldehyde(also called Benzenecarbonal) is the simplest representative of the aromatic aldehydes. It is a colorless liquid aldehyde with a characteristic almond odor. It boils at 180°C, is soluble in ethanol, but is insoluble in water. Benzaldehyde is formed by partial oxidation of benzyl alcohol and readily oxidized to benzoic acid and is converted to addition products by hydrocyanic acid or sodium bisulfite. It is also prepared by oxidation of toluene or benzyl chloride or by treating benzal chloride with an alkali, e.g., sodium hydroxide. It is used chiefly in the synthesis of other organic compounds, ranging from pharmaceuticals to plastic additives and benzaldehyde is an important intermediate for the processing of perfume and flavouring compounds and in the preparation of certain aniline dyes . It is the first step in the synthesis for fragrances. It undergoes simultaneous oxidation and reduction with alcoholic potassium hydroxide, giving potassium benzoate and benzyl alcohol. It is converted to benzoin with alcoholic potassium cyanide, with anhydrous sodium acetate and acetic anhydride, giving cinnamic acid. Compounds which do not have alpha-hydrogen atoms cannot form an enolate ion and do not undergo electrophilic alpha-substitution and aldol condensation. Aromatic aldehydes such as benzaldehyde and formaldehyde may undergo disproportionation in concentrated alkali (Cannizaro's reaction); one molecule of the aldehyde is reduced to the corresponding alcohol and another molecule is simultaneously oxidized to the salt of a carboxylic acid. The speed of the reaction depends on the substituents in the aromatic ring. Two different types of aldehydes (aromatic and aliphatic) can undergo crossing reaction to form fomaldehyde and aromatic alcohols. 2-Chloro-6-fluoro-Benzaldehyde, halogenated aromatic aldehydes, is used as an intermediate for organic synthesis. 2-Chloro-6-fluorobenzaldehyde is used as an intermediate for the synthesis of pharmaceuticals and pesticides. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to yellow solid | |
|
ASSAY |
99.0% min | |
| MELTING POINT | 35 - 38 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | 200kgs in drum | |
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26/37/39 | ||
|
|
|