PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
54 - 56 C
|
|
|
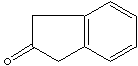
| 2-INDANONE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 615-13-4 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 210-410-3 | |
| FORMULA | C9H8O | |
| MOL WT. | 132.16 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | 1,3-Dihydro-2H-inden-2-one; beta-Hydrindone; Indan-2-one; | |
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | 54 - 56 C (Decomposes) | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | ||
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY | ||
|
AUTOIGNITION |
| |
|
NFPA RATINGS |
||
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
||
| FLASH POINT | 100 C | |
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| ndene is a clear to yellowish liquid ; boils at 181C and melts at -2 C. It is a polynuclear hydrocarbon compound with a five-membered ring fused to benzene ring. Indan, 2,3-dihydroindene, is a clear to yellowish liquid; boiling point 177 C; insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and ether. They are obtained from coal tar distillation; used as solvents, raw material for synthetic resins and to make other organic compounds such as pharmaceutical ingredients and agrochemicals especially plant growth regulators. Some indane compounds have the characteristic odour and are used for the preparation of perfumes and flavouring agents. Indanone is a ketone form of indane. A main industrial application of indene is the production of indene/cumarone thermoplastic resin. There are position isomers, 1-indanone and 2-indanone. Indanone is known as an important drug intermediate for serotonin reuptake inhibitors and others. Oxime is any compound with the general formula R\R'/C=N-OH, where R and R' are hydrogen atoms or organic groups derived by removal of a hydrogen atom from an organic compound. Oximes are condensation products of hydroxylamines with aldehydes (forming aldoxime), ketones (forming ketoxime), or quonone. There are two geometrical isomer: syn and anti isomer (the term syn-anti isomerism is for stereoisomers by other atoms' unsaturated bond rather than carbon). Two isomers have very different properties. Oximes are converted into corresponding amides by reaction of Beckmann rearrangement (usually using sulphuric acid as a catalyst). Oximes are used as chemical building block for the synthesis of agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals. Indanedione is the nucleus of synthetic anticoagulants for the treatment of disorders in which there is excessive or undesirable clotting, such as thrombophlebitis, pulmonary embolism, and certain cardiac conditions. They inhibits the hepatic synthesis of the vitamin K–dependent coagulation factors. Anticoagulants act as rodenticide by causing massive hemorrhaging. Indanedione class anticoagulants or rodenticides include diphenadione, phenindione, pindone, and valone. Indane class compounds show various functions such as light and temperature sensitivity, heat resistance, conductivity, emittability, corrosion resistance and detection of amino groups. They are used in the applications of thermo and light sensitizer, liquid crystal chemistry, optical brightening agents, luminescence chemistry, spectrophotometric analysis, molecular chemistry, organometallic-complexes and biochemorphology industry. Indane class compounds can create perfumes, aroma chemicals or fragrance enhancers. They also contribute to the development of drugs having analgesic, anaesthetic and sedative properties, and antibiotics. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white crystals | |
| PURITY |
99.0% min |
|
| MELTING POINT |
54 - 56 C |
|
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING | ||
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 22-24/25 | ||
|
|
|