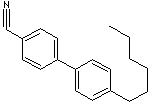
| CAS
NO. |
41122-71-8 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
255-229-0 |
| FORMULA |
C20H23N |
| MOL
WT. |
277.40 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
4'-Heptyl[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-carbonitrile; |
|
4'-Heptil[1,1'-bifenil]-4-carbonitrilo;
4'-Heptyl[1,1'-biphényl]-4-carbonitrile; 4-Cyano-4'-heptylbiphenyl; |
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white crystals |
| MELTING
POINT |
|
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
| AUTOIGNITION |
|
| NFPA
RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
| Nitrile is an organic compounds containing cyano group (-C≡N, containing
trivalent nitrogen) which is attached to one carbon atom with the general
formula RC≡N. Their names are corresponding to carboxylic acids by changing '-ic
acid' to the suffix, '-onitrile' which denotes only the ≡N atom (triply bound)
excluding the carbon atom attached to it, or the suffix, '-carbonitrile' where
the carbon atom in the -CN is included, whichever preserves a single letter O.
Examples are acetonitrile from acetic acid and benzonitrile from benzoic acid.
The prefix, 'cyano-' is used as an alternative naming system to indicate the
presence of a nitrile group in a molecule for the compounds of salts and
organic derivatives of hydrogen cyanide (HC≡N). Isocyanides are salts and hydrocarbyl
derivatives from the isomer, HN+≡C-.
Cyanoacetic acid, the half
nitriled-malonic acid, and its esters are basic chemical intermediates
for the production of;
- Malonates
- Barbitals
- Caffeine,
Betaine, Vitamin B
- Pharamceuticals
- Glycine
- Surfactancts
- Agrochemicals
- Dyestuffs
- Adhesives
- Indigo
dyes
- Herbicides
- Engineering
plastics
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white crystals |
|
PURITY
|
99.0%
min
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 20/21/26-36/37/38, Safety
Phrases: 26-36 |
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF BIPHENYL
|
| Biphenyl (also
called Diphenyl, but exactly one of two compounds. The other is o-phenylphenol,
used to prevent the growth of moulds ) is an aromatic hydrocarbon; molecule
structure is composed of two six-sided carbon rings connected at one carbon site
on each ring. Pure biphenyl is a toxic colourless crystalline solid with a
pleasant odour; melting point 70 C, boiling point 255 C, which gives plates or
monoclinic prismatic crystals; it is insoluble in water but soluble in ordinary
organic solvents. It is directly used in the preservation of citrus fruits as a
fungistat in transportation containers. It is a raw material for polychlorinated
diphenyls (PCB) in which chlorine replaces hydrogen in biphenyls. There are 209
chlorinated isomers of biphenyl theoretically. But PCBs are referred to the
biphenyl compounds with one to ten chlorine substitutions. PCBs are used
heat-transfer agents and as electric insulators that block the flow of electric
current across in electrical equipments. They are known as environmental
pollution materials which are accumulated in animal tissues and cause toxic
effects including carcinogenesis. Biphenyl is used as an intermediate for the
production of a wide range of organic compounds (e.g. emulsifiers, optical
brighteners, crop protection products, plastics), as a heat transfer medium
alone or with diphenyl ether in heating fluids, as a dyestuff carrier for
textiles and copying paper and as a solvent in pharmaceutical production. Aminodiphenyls
are used as rubber
antioxidants and intermediates for the synthesis of
organic compounds ( azo dyes and pharmaceuticals). Biphenyl derivatives
are used as an intermediate for the synthesis of organic
compounds including pharmaceuticals, antifungal agents,
optical
brightening agents and dyes.
Biphenyl compounds also used in luminescence
chemistry, spectrophotometric analysis, molecular
chemistry, and as a stating material
for organometallic-complexes. |
