| CAS
NO. |
1193-21-1
|
|
| EINECS
NO. |
214-770-2 |
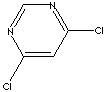
| FORMULA |
C4H2Cl2N2 |
| MOL
WT. |
148.97 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
pyrimidine,
4,6-dichloro; |
|
4,6-Dichloro Pyrimidin;
4,6-Dichloropirimidina (Italian);
|
| SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
yellow
semi-solid |
| MELTING POINT |
64
- 66 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
176
C |
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
Pyrimidine is a heterocyclic compound containing nitrogen atoms at positions 1
and 3 in six-membered ring structure molecule. The simplest one is Pyrimidine
itself and the three major Pyrimidines in living systems are cytosine, thymine, and
uracil. Pyrimidine and its derivatives are biologically important components of
nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. They can be the parent compound of many
drugs, including the barbiturates. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
yellow
semi-solid |
|
ASSAY
|
97.0%
min
|
|
MELTING POINT |
64
- 66 C |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
Hazard
Symbols: Risk Phrases: 34-36/37, Safety Phrases: 26-36/37/39-45 |
