PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
2924.29
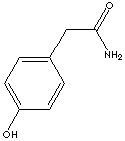
2-(p-Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide; p-(Carbamoylmethyl)phenol; 4-Hydroxyphenylacetamide
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
176 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
4-(Hydroxyphenyl)acetamide is used as an intermediate for organic compounds and pharmaceuticals ( especially for Atenolol)
APPEARANCE
98.5% min
MELTING POINT
174 C min
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
Atenolol, chemically 4 -[2'-hydroxy-3'-[(1- methylethyl) amino] propoxy]- benzeneacetamide, is a cardioselective beta blocker used to control abnormal heart rhythms, to treat angina, and to reduce high blood pressure. Beta blocker is a drug blocking nerve impulses to special sites (beta receptors) in the cerebellum and reduces the rate of heartbeats and the force of heart contractions. Other beta blockers include acebutolol, betaxolol, bisoprolol, oxprenolol, propranolol, and sotalol.