PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
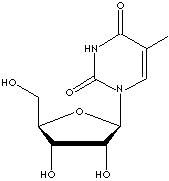
5-Methyl-1-(��-L-ribofuranosyl)-2,4(1H,3H)-pyrimidinedione;
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan- 2-yl]-5-methylpyrimidine- 2,4-dione; Ribothymidine; Other RN:849658-09-9
CLASSIFICATION
Pyrimidinedione, Riboside, Nucleoside
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white to off-white crystalline powder
183 - 187 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Thymine riboside
PubChem Compound Summary - Ribothymidine
Drug Bank - 5-Methyluridine
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Ribothymidine
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/ - Ribothymidine
Local:
Ribose
is a pentose (five-carbon sugar) that is a component
of the ribonucleic acid (RNA), where it alternates with
phosphate groups to form the 'back-bone' of the RNA
polymer and binds to nitrogenous bases. Ribose phosphates
are components of the nucleotide coenzymes and are utilized
by microorganisms in the synthesis of the amino acid
histidine. Its close relative, deoxyribose, is a constituent
of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), where it alternates
with phosphate groups to form the 'back-bone' of the
DNA polymer and binds to nitrogenous bases. The presence
of deoxyribose instead of ribose is one difference between
DNA and RNA. Ribose has one more oxygen atom in its
molecule than deoxyribose. Ribose has a five member
ring composed of four carbon atoms and one oxygen. Hydroxyl
groups are attached to three of the carbons. The other
carbon and a hydroxyl group are attached to one of the
carbon atoms adjacent to the oxygen. In deoxyribose,
the carbon furthest from the attached carbon is stripped
of the oxygen atom in what would be a hydroxyl group
in ribose. The sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) molecules
in the nucleic acid are all oriented in the same direction.
Their carbon atoms are numbered: the 5' carbon atom
is always on the side of the sugar molecule that faces
the leading end, while the 3' carbon atom always faces
the tail end. Nucleotide is the structural unit of a
nucleic acid. A nucleotide consists of either a nitrogenous
heterocyclic base (purine or pyrimidine) , a pentose
sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) and a phosphate group
attached at the 5' position on the sugar. A nucleoside
consists of only a pentose sugar linked to a purine
or pyrimidine base, without a phosphate group. Purine
bases are Adenine, Guanine and Hypoxanthine (examples
of purine nucleosides are Adenosine, 2'-Deoxyadenosine,
Guanosine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine, Inosine, 2'-Deoxyinosine).
Pyrimidine bases are Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil (examples
of pyrimidine nucleosides are Cytidine, 2'-Deoxyguanosine,
5-Methyluridine, 2'-Deoxy-5-Methyluridine, Uridine,
2'-Deoxyuridine). The nucleoside derivatives are involved
in important functions in cellular metabolism and are
used to synthesize enzyme inhibitors, antiviral agents,
and anticancer agents.
|
|
- Urasil: a pyrimidine base
- Uridinea pyrimidine nucleoside
- Uridine Monophosphate (UMP, Uridylic acid): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of uridine; a component of ribonucleic acid.
- Uridine Diphosphate (UDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-pyrophosphate of uridine; acting as the chief transferring coenzyme in carbohydrate metabolism; acting as a carrier of hexoses, hexosamines, and hexuronic acids which are intermediates in the metabolism.
- Uridine Triphosphate (UTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of uridine; acting as a precursor in the synthesis of ribonucleic acid and of UDP-linked intermediates.
- Deoxyuridine Monophosphate (dUMP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate. (deoxy-, also called desoxy, is a prefix for the designation of compounds which contain one less atom of oxygen than the reference substance).
- Deoxyuridine Diphosphate (dUDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxythymidine triphosphate.
- Deoxyuridine Triphosphate (dUTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of deoxyuridine; an intermediate in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides.
Thymine is a pyrimidine base, occurring condensed with deoxyribose to form the nucleoside deoxythymidine in animal cells. Thymidine is significant because of its involvement in the biosynthesis of DNA and in the preservation and transfer of genetic information. It was thought that there is no thymine in ribonucleic acid (RNA); the thymine nucleotides contain only deoxyribose. However, It is now known that thymine, produced from uracil by post-transcriptional methylation, occurs as a rare base in rRNAs and tRNAs. When N1 is linked to the C1 of ribose, thymine forms a pyrimidine nucleoside called thymidines which are phosphorylated with from one to three phosphoric acid groups to form the three nucleotides; thymidine monophosphate(TMP), thymidine diphosphate(TDP), and thymidine triphosphate (TTP) respectively. When N1 is linked to the C1 of deoxyribose, deoxy nucleosides and nucleotides are formed from thymine and deoxyribose; deoxythymine monophosphate (dTMP), deoxythymine diphosphate (dTDP), and deoxythymine triphosphate (dTTP). TTP is involved in the formation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as a donator of phosphate groups to adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
- Thymine: a pyrimidine base
- Thymidine: a pyrimidine nucleoside
- Thymidine Monophosphate (TMP, Thymidylic acid): a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of thymidine.
- Thymidine Diphosphate (TDP): a nucleotide, the 5'-pyrophosphate of thymidine
- Thymidine Triphosphate (TTP): a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of thymidine.
- Deoxythymidine Monophosphate (dTMP), a nucleotide, the 5'-phosphate of deoxythymidine. (deoxy-, also called desoxy, is a prefix for the designation of compounds which contain one less atom of oxygen than the reference substance).
- Deoxythymidine Diphosphate (dTDP), a nucleotide, the 5'-pyrophosphate of deoxythymidine.
- Deoxythymidine Triphosphate (dTTP), a nucleotide, the 5'-triphosphate of deoxythymidine; a precursor in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleic acid.
Chemically modified nucleotides substituted or attached by special chemical groups or elements are studied and used to inactivate the normal biological operation in the living organism and the function of important enzymes.
APPEARANCE
fine off-white crystalline powder
98.0 - 102.0 %
MELTING POINT
183 - 187 C