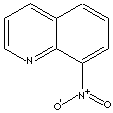
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
The prefix nitro- indicates the presence of NO2- radical, while nitrate refers to any salt or ester of nitric acid or the NO3- anion. Nitroso- is the prefix indicating presence of the group -NO and azo- is for -N=N- group. Some range of organic compounds containing nitrogen include nitro compounds (RNO2 ), nitroso compounds (RNO), amines (R3N ), amino acids, and natural alkaloids or nucleotides. The nitrogen ion in nitro compounds is trigonally planar with 120° angles. There are two resonance bonds so that the two oxygens are equivalent. Nitro compounds are strongly basic due to electron withdrawing both inductively and mesomerically. Historically, they are abundant in dyes and explosives. Nitro compounds, organic hydrocarbons having one or more NO2 groups bonded via nitrogen to the carbon framework, are versatile intermediate in organic synthesis.
- Michael addition
- Reduction
- Henry Reaction (Nitro-aldol reaction)
- Nef reaction
- O-Alkylation
- Cycloaddition
- Substitution, Elimination, Conversion reaction
- Alkylation, Acylation, and Halogenation
Nitro compounds are readily reduced into amines when reacted with hydrochloric acid. Aromatic nitro compounds also yield anilines, aromatic amine componds. Nitro compounds are cleaved into two parts by the addition of a molecule of water to produce carbonyl compounds (aldehydes or ketones). Aromatic nitro compounds undergo nucleophilic substitutions to be replaced by the hydroxide anion, resulting in the creation of phenol compounds and by alkoxy nucleophiles to corresponding ethers.
APPEARANCE
CONTENT
99.0% min
MELTING POINT