PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
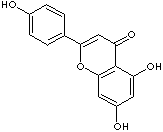
208-292-3
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
SMILES
c12c(oc(c3ccc(O)cc3)cc1=O)cc(O)cc2O
CLASSIFICATION
Flavone
EXTRA NOTES
Other RN: 461015-54-3
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
315 C
Practically insoluble (183 mg/l at 25 C)
Soluble in DMSO, slightly soluble in hot ethanol
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Apigenin
Google Scholar Search - Apigenin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Apigenin
PubChem Compound Summary - Apigenin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Apigenin
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Apigenin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Apigenin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous Substances Data Bank - Apigenin
SigmaAldrich
A plant flavonoid that has been found to inhibit cell proliferation by arresting the cell cycle at the G2/M phase. Inhibition of growth through cell cycle arrest and induction of apoptosis appear to be related to induction of p53.Inhibits PMA-mediated tumor promotion by inhibiting protein kinase C1 and the resulting suppression of oncogene expression. It has also been reported to inhibit topoisomerase I-catalyzed DNA re-ligation and enhance gap junctional intercellular communication.
Local
Apigenin is a bioflavone, considered to have a bioactive effect on human health
as antioxidant, radical scavenger, anti-inflammatory, carbohydrate metabolism promoter, immunity
system modulater.
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
80.0% min ( 98.0% 95.0%, 90.0% min)
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
2.0% max
LOSS ON DRY
5.0% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
LEAD
10ppm max
ARSENIC
2ppm max
SOLVENTS RESIDUE
1000ppm max (ethanol)
PESTICIDES RESIDUE
100ppb max
MICROBIOLOGICALS
Total
Aerobic: 1000 CFU/g max
E. Coli: negative
Salmonella:
Negative
Mold and Yeast: 100 CFU/g
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FLAVONOID
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin.
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]() Xi
Xi
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36
PRICE INFORMATION