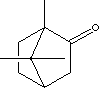
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
204 C
5.24
AUTOIGNITION
870 C
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
|
|
Menthol (Peppermint Camphor): ) a white crystalline compound with a characteristic pungent odor; freely soluble in alcohols, ether, and chloroform. It is obtained from mint oils (mainly peppermint) or made synthetically from coal tar. It exists in levo or dextro isomer forms. Menthol imparts a tingling sensation to the skin and used in skin fresheners like after-shave and suntan lotions. It has a local anesthetic property for short-term relief of minor sore throat and minor muscle aches. It is used in medicines and perfumes, and as a mint flavoring agent. End applications include toothpaste, cough drops, ice cream, chewing gum, shampoo, medical plaster.
Thymol (Thyme Camphor): a white crystals with camphor like odor, is a phenolic compound obtained naturally from thyme oil (or other volatile oils) or prepared synthetically. It is very slightly soluble in water; soluble in paraffin oil and alcohol. It is used as a stabilizer in pharmaceutical and as a topical antiseptic, antibacterial, and anti-fungal agent. It is also used as a flavoring agent for drugs (camphor, herbal, wintergreen,disinfectants, origanum )
Wikipedia Linking:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Camphor
http://chestofbooks.com/.....Camphor can be isolated from the volatile oils containing it by freezing, if
necessary after fractionation. It consists of a granular-crystalline, colorless,
translucent mass with a decided tendency toward sublimation. It has a
characteristic odor and is readily soluble in organic solvents. When cast on
water, small pieces rotate in a very lively manner. By various observers its
properties have been recorded as follows: d18o 0,9853 (determined for
/-camphor);4) m. p. 176,3 to 176,5°; b. p. 209,1° (759 mm., mercury completely
within the vapor);5) m. p. 178,4°; [a]D + 41,44° and - 42,76°;6) m. p. 175°; b.
p. 204°;7) m. p. 175°; b. p. 204°; [a]D + 44,22° in 20 p. c. alcoholic
solution.8)
The world's consumption of camphor is very large, for the
manufacture of celluloid ware alone enormous quantities are used. It is also
used extensively in the manufacture of smokeless powder, for disinfection and
for medicinal purposes. This great demand has given rise to its synthetic
production from turpentine spirits on a commercial scale. In general, one of two
methods is followed: Either pinene is converted into bornyl chloride by means of
hydrogen chloride, which by way of cam-phene and Isoborneol is changed to
camphor; or pinene is directly converted into esters of borneol or isoborneol.
TECH GRADE
APPEARANCE
white crystals
CONTENT
96.0% min
MELTING POINT
168 - 179 C
NONVOLATILES
0.5% max
BP/USP
APPEARANCE
white crystals
CONTENT
96.0% min
OPTICAL ROTATION
-1.5 ~ +1.5 °
MELTING POINT
172 - 180 C
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF TERPENE
|
Class |
number of isoprene |
Examples |
|
Hemiterpene |
1 (C5H8) |
Found in associated with Alkaloids, Coumarins and Flavonoids. |
|
Monoterpenes |
2 (C10H16) |
Geraniol, Citronellol, Pinene, Nerol, Citral, Camphor, Menthol, Limonene, Thujone |
|
Sesquiterpenes |
3 (C15H24) |
Nerolidol, Farnesol |
|
Diterpenes |
4 (C20H32) |
Phytol, Vitamin A1 |
|
Triterpenes |
6 (C30H48) |
Squalene |
|
Tetraterpenes |
8 (C40H84) |
Carotene (Provitamin A1) |
|
Polyterpenes |
>10 (C5H8)n |
|