PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
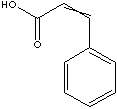
c1(\C=C\C(O)=O)ccccc1
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
FEMA No. 2288
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
132 - 135 C
Health hazard: 2, Fire: 1, Reactivity Hazard: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
Google Scholar Search - Cinnamic acid
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Cinnamic acid
PubChem Compound Summary - Cinnamic acid
IPCS INCHEM - Cinnamyl Alcohol and Related Substances
Drug Bank - Cinnamic acid
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Cinnamic acid
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Cinnamic acid
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Cinnamic acid
Local:
In
biological chemistry, cinnamic acid is a key intermediate in shikimate and phenylpropanoid pathways.
Shikimic acid is
a precursor of many alkaloids, aromatic amino acids, and indole derivatives.
Phenylpropanoid are a class of plant metabolites based on phenylalanine. They are widely distributed in plants fulfilling many functions including plant
defense mechanism, pigmentation and external signaling
system. Phenylalanine is first converted to cinnamates, coumarines, caffeic acids, ferulic acids, and sinapic
acids. Cinnamic acid is the precursor of
these acids. Cinnamic acid is
the parent compound of its esters which are more volatile
to
be transported to other parts easily.
Commercial cinnamic acid, a phenylacrylic acid structure
compound, is used in converting to its esters such as
methyl, ethyl, and benzyl cinnamate for the perfume and
flavour application. Cinnamic acid
and Its derivatives including esters and carboxylic functional derivatives
are used as important components in
flavours, perfumes, synthetic indigo and pharmaceuticals. Cinnamate can
act as optical filters or deactivate substrate molecules that have been excited
by light for the protection polymers and organic substances. They, cosmetic
grades, are used as sunscreen agents to reduce skin damage by blocking UV-A, B.
Cinnamic acid is an odorless white crystalline powder;
slightly soluble in water; melting point 133 C
and boiling point
300 C.
APPEARANCE
99.0% min
132 - 135 C
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
ARSENIC
2ppm max
20ppm max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May cause eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Respiratory system, eyes, skin.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36