PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
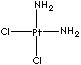
[Pt+2]([NH3])([Cl-])([Cl-])[NH3]
CLASSIFICATION
Antineoplastic agent, Cross-linking reagent, Indicator, Radiation-sensitizing agent, Platinum Complexes
EXTRA NOTES
An inorganic and water-soluble platinum complex. After undergoing hydrolysis, it reacts with DNA to produce both intra and interstrand crosslinks. These crosslinks appear to impair replication and transcription of DNA. The cytotoxicity of cisplatin correlates with cellular arrest in the G2 phase of the cell cycle.
Overall Carcinogenic Evaluation: Group 2A
Other RN: 96081-74-2, 936542-99-3
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
SOLVENT SOLUBILITY
Insoluble in most organic solvents. Soluble in DMF.
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/
Google Scholar Search: http://scholar.google.co.kr/
http://www.iupac.org/
The mechanism of action of platinum anti-tumor drugs. Abstract. A discussion is presented on the mechanism of action of platinum amine compounds, used as antitumor drugs. The relationship between biological acitivity and structure of the compounds is discussed, with special attention to the nature of the ligands coordinated to platinum. The primary biological target appears to be the interaction with nucleic acids, and therefore studies of the interaction of platinum amine compounds (both active and inactive ones) with nucleic acids and nucleic acid fragments are of great interest. Studies on mononucleotides have made clear that a strong preference exists for platinum binding at guanine—N7 sites. Investigations on oligonucleotides have shown that, when two neighboring guanines are present, chelation of the cis—Pt(NH3)2 unit (abbreviated cisplatin) is strongly preferred above all other possibilities. Studies on DNA ( in vivo and in vitro) have made clear that similar binding modes occur in DNA and oligonucleotides, and that - after cisplatin binding — the DNA structure is distorted in the same way as double-stranded oligonucleotides.
http://www.medclip.com/
Medical Videos - CisPlatin: Mechanism of Action
Local
Carboplatin, a platinum coordination compound which contains a platinum atom surrounded with two ammonia groups and two other ligands in a ring structure. Cisplatin is an analogue which has two chloride atoms instead of ring structure. Oxaliplatin contains a platinum atom complexed with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane and with an oxalate ligand as a leaving group. It is known that diaminocyclohexane group contributes greater cytotoxicity than cisplatin and carboplatin. Oxaliplatin is not generally cross-resistant to cisplatin or carboplatin. They are capable of forming platinum complexes producing inter- and intrastrand DNA crosslinks with neighboring guanine residues, resulting in DNA-mismatch repair (MMR) activity in the cancer cells. Carboplatin has less nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity and emetogenesis and more stability than cisplatin. They, platinum-based antineoplastics, have a broad spectrum of antitumor activity in the treatments of carcinomas of ovarian, testicular, bladder, small and non–small cell lung, head and neck carcinoma, and seminoma. They are synergistic with fluorouracil. They are radiation sensitive. The chemical designation of cisplatin is (SP-4-2)-diaminedichloroplatinum (II). It is a yellow crystalline powder; soluble in water and saline; administered intravenously. The chemical designation of carboplatin is (SP-4-2)-diammine [1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato (2-)-0, 0']- platinum (II). It is a white crystalline powder; soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol, acetone, and dimethylacetamide; administered intravenously. The chemical designation of oxaliplatin is SP-4-2-(1R-trans))- (1,2-cyclohexanediamine-N,N')- (ethanedioato(2-)-O,O') platinum (II). It is a white crystalline powder; soluble in water; very slightly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ethanol, hexane, benzene and acetone.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies Test A,B
ASSAY
98.0 - 102.0% (HPLC)
PLATINUM CONTENT
64.4 - 65.2%
RELATED SUBSTANCE
1.0% max (Trichloroammineplatinate)
WATER
1.0% max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ALKYLATING AGENTS AS ANTITUMOR
- Nitrogen mustard
- Chlorambucil (CAS RN: 305-03-3)
- Mechlorethamine (CAS RN: 51-75-2)
- Melphalan (CAS RN:148-82-3)
- Uracil Mustard (CAS RN: 66-75-1)
- Cyclophosphamide (CAS RN: 50-18-0)
- Iphosphamide (CAS RN: 3778-73-2)
- Nitrosoureas
- Triethylenemelamine (CAS RN: 51-18-3)
- Hexamethylmelamine (CAS RN: 645-05-6)
- Bis-chloroethylnitrosourea (CAS RN: 154-93-8)
- Chloroethylcyclohexylnitrosourea (CAS RN: 13010-47-4)
- Streptozotocin (CAS RN: 18883-66-4)
- Platinum compounds
- Carboplatin (CAS RN: 41575-94-4)
- Oxaliplatin (CAS RN: 61825-94-3)
- Cisplatin (CAS CN: 15663-27-)
- Tetraplatin (CAS RN: 62816-98-2)
- (Carboxyphthalato)platinum (CAS RN: 65296-81-3)
- Alkyl sulfonates
- Busulfan (CAS RN: 55-98-1)
- Mannosulfan (CAS RN: 7518-35-6)
- Treosulfan (CAS RN: 299-75-2)
- Aziridines
- Thiotepa (CAS RN: 52-24-4)
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Harmful if swallowed or in contact with skin. May cause an allergic skin reaction. Harmful if inhaled. May cause allergy or asthma symptoms or breathing difficulties if inhaled. May damage fertility or the unborn child. OSHA Hazards:Target Organ Effect, Toxic by inhalation., Toxic by ingestion, Harmful by skin absorption., Skin and respiratory sensitizer, Teratogen. Target Organs: Bone marrow, ears, Kidney, Nerves., Liver injury may occur., Kidney injury may occur.
GHS
Danger
PICTOGRAMS



HAZARD STATEMENTS
H300-H318-H350
P STATEMENTS
P201-P264-P280-P301 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338-P308 + P313
![]() T
T
RISK PHRASES
45-25-41
SAFETY PHRASES
53-26-39-45