PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
O([C@H]1[C@@](C[C@H](C([C@@H]([C@H]([C@](C)(O)[C@H](OC( [C@@H]([C@H]([C@@H]1C)O[C@@H]1C[C@@]([C@@H](O)[C@@H]( O1)C)(OC)C)C)=O)CC)O)C)=O)C)(OC)C)[C@@H]1[C@@H]([C@@H ](C[C@@H](O1)C)N(C)C)O
CLASSIFICATION
Antibacterial, Antibiotic, Anti-infective Agent, Gastrointestinal Agent, Macrolide
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
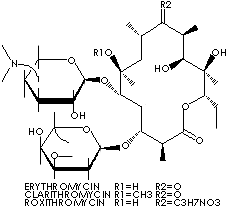
The macrolides, derived from Streptomyces bacteria, are a group of antibiotics that inhibits protein synthesis by bacteria at the 50S ribosome. They are characterized by a macrocyclic ring (a large ring molecule with many functional groups bonded to it) and a large lactone ring in the molecular structure. They are usually used for respiratory tract, skin, and genitourinary infections. Erythromycins inhibits protein synthesis in some microorganisms and are used as an antibiotic against many kinds of infections caused by gram-positive bacteria, including some beta-hemolytic streptococci, pneumococci and staphylococci as well as gram-negative bacteria and some fungi. It is used also in the treatment of upper and lower respiratory tract infections caused by chlamydia trachomatis and intestinal amebiasis. It's application include the treatment of syphillis in patients who may be allergic to penicillin and the treating Legionnaire's disease. Clarithromycin,6-0-methylerythromycin, has a close structural and biological similarity to with erythromycin.It is effective against a broad spectrum of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. It is used to treat respiratory tract infections and soft tissue infections. It is used to treat duodenal ulcer associated with Helicobacter pylori infections in combination with omeprazole. One common feature of clarithromycin appears to be the stability against acids. It is absorbed and diffused easily into tissues and phagocytes without being protected from gastric acids. It is more effective against certain gram-negative bacteria, such as Legionella pneumophilae than erythromycin. Clarithromycin is a white to off-white crystalline powder; insoluble in water; soluble in acetone, slightly soluble in alcohol and acetonitrile; administered orally.
Examples of macrolides are:
- Azithromycin (CAS RN: 83905-01-5)
- Brefeldin A (CAS RN: 20350-15-6)
- Clarithromycin (CAS RN: 81103-11-9)
- Erythromycin (CAS RN: 114-07-8)
- Erythromycin Estolate (CAS RN: 3521-62-8)
- Erythromycin Ethyl Succinate (CAS RN: 1264-62-6)
- Erythromycin Stearate (CAS RN: 643-22-1)
- Josamycin (CAS RN: 16846-24-5)
- Kitasamycin (CAS RN: 1392-21-8)
- Lincomycin Hydrochloride (CAS RN: 859-18-7)
- Mepartricin (CAS RN: 11121-32-7)
- Midecamycin (CAS RN: 35457-80-8)
- Oleandomycin Phosphate (CAS RN: 7060-74-4)
- Oleandomycin Triacetate (CAS RN: 2751-09-9)
- Rokitamycin (CAS RN: 74014-51-0)
- Roxithromycin (CAS RN: 80214-83-1)
- Spiramycin (CAS RN: 8025-81-8)
- Tylosin (CAS RN: 74610-55-2)
- Tylosin Tartrate (CAS RN: 74610-55-2)
- Virginiamycin M (CAS RN: 21411-53-0)
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Clarithromycin
http://www.biomed.cas.cz/
Clarithromycin
Inhibits Myometrial Contractions in Isolated Human Myometrium Independent
of Stimulus
Summary: Erythromycin has a well-known dual effect
on the contractility of the gastrointestinal system and recently
has also been shown to inhibit contractions of the rat myometrium.
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effects of clarithromycin
on oxytocin, prostaglandin F2�� (PGF2��) and KCl-induced contractions
of human myometrium in vitro. Myometrial strips were obtained from
pregnant women undergoing elective Cesarean section and the strips
were suspended in a jacketed organ bath filled with Krebs solution
at 37 oC (pH 7.4) and continuously aired with 95 % oxygen and 5
% carbon dioxide. Isometric contractions were measured using a force
displacement transducer. Oxytocin, PGF2��, KCl and clarithromycin
were applied to the tissue bath and the amplitude and frequency
of contractions were evaluated at 20-min intervals. Freidmann analysis
of variance, Kruskal Wallis and Wilcoxon Rank tests were used for
statistical analysis of the data. Clarithromycin dose dependently
inhibited the amplitude of contractions independent of the stimulus.
Pre-treatment with apamin prevented clarithromycin-induced effects
on amplitude and frequency of contractions. We conclude that the
macrolide antibiotic clarithromycin may have a direct inhibitory
effect on contractions of human myometrium.
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Clarithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic. It prevents bacterial growth by
interfering with protein synthesis. Clarithromycin is an acid-stable version of
erythromycin and is particularly effective against gram-negative
bacteria.1 It has a short half-life, however its
metabolite, 14-hydroxy clarithromycin is nearly twice as active as
clarithromycin against certain bacteria.
|
|
APPEARANCE
Complies
OPTICAL ROTATION
-89° ~ -95°
8.0 - 10.0
1.0% max
LOSS ON DRYING
3.0% max
20ppm max
PRICE INFORMATION