| CAS
NO. |
25122-41-2
(Base)
25122-46-7 (17-propionate) |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
246-633-8,
246-634-3 |
| FORMULA |
C25H32ClFO5 |
| MOL
WT. |
466.98 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
|
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
Clobetasole propionate; Dermoval; Dermovate; Dermoxin; |
|
11b,16b)-21-Chloro-9-fluoro-11-hydroxy-16-methyl-17
(1-oxopropoxy)-pregna-1,4-diene-3,20- dione; Temovate;
|
|
SMILES |
|
|
CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL
AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
White
crystalline powder |
| MELTING
POINT |
195
- 197C (decomposes) |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC
GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR
DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
Health:
2 Flammability: 0 Reactivity: 0 |
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
GENERAL
DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
|
|
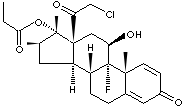
Clobetasol, a synthetic glucocorticoid, an analogue of prednisolone derived from
cortisol, having activity in replacement therapy for adrenal insufficiency and
as an antiinflammatory and immunosuppressant. Clobetasol has a powerful activity
of corticosteroids with a slight mineralocorticoid activity. It is used to for
the relief of inflammation and pruritus in corticosteroid-responsive dermatoses.
The propionate of clobetasol is a white to off-white crystalline powder;
insoluble in water; melting point 195 - 197 C. The chemical designation
(11b,16b)-21-chloro-9-fluoro-11-hydroxy-16-methyl-17
(1-oxopropoxy)-pregna-1,4- diene-3,20- dione.
|
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
white
to off-white crystalline powder |
|
IDENTIFICATION
|
Complies
|
|
ASSAY
|
97.0
- 103.0%
|
|
OPTICAL
ROTATION
|
+98°
~ +104°
|
|
RELATED
SUBSTANCE
|
|
|
LOSS
ON DRYING
|
0.5%
max
|
|
SULFATED
ASH
|
0.1%
max
|
|
RESIDUE
OF SOLVENT
|
0.2%
max
|
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
|
| HAZARD
CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
| Hazard Symbols: XN, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38,
Safety
Phrases: 26-36 |
| GENERAL
DESCRIPTION OF CORTICOSTEROID
|
Corticosteroid is a synthetic or naturally occurring 21-carbon steroid
structure substances with four fused rings and vary functional branches attached to the ring
system. Cholesterol and steroid hormones have this carbon skeleton. The term steroid
refers to these three groups that contain a hydrogenated
cyclopentano perhydro phenanthrene ring system. In restricted context for medical
usage by non-endocrinologists, it refers to corticosteroids. Natural corticosteroids are elaborated by the adrenal
cortex in response to physiological carbohydrate metabolism. According to their
predominant biologic activity, they are divided into two major groups:
glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid. Glucocorticoid's chief function is to
regulate carbohydrate, lipid, and protein metabolism and inhibit the release of
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone). Glucocorticoids also affect muscle tone and
the microcirculation, participate in the maintenance of arterial blood pressure,
increase gastric secretion, alter connective tissue response to injury, impede
cartilage production, inhibit inflammatory, allergic, and immunologic responses,
invoke shrinkage of lymphatic tissue, reduce the number of circulating
lymphocytes, and affect the functions of the central nervous system. In humans,
the most important ones are cortisol, cortisone, and corticosterone.
Mineralocorticoids, uniuqely aldosterone in human, regulate the balance of water
and promote retention of sodium, loss of potassium. Aldosterone plays a role also
in promoting tissue repair. Spironolactone is the aldosterone antagonist called
potassium-sparing diuretic used in the treatment of hypertension.
Corticosteroids are used in clinically for hormonal replacement therapy, for
suppression of ACTH, as antineoplastic, antiallergic, and anti-inflammatory
agents, and to suppress immune responses.
- Glucocorticoid
Receptor Agonists
- Dexamethasone
- Triamcinolone
- Hydrocortisone
- Prednisone
- Glucocorticoid
Receptor Antagonists
- Mineralocorticoid
Receptor Agonists
- Mineralocorticoid
Receptor Antagonists
- Spironolactone
- Eplerenone
|
