PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
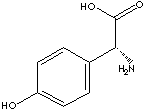
N[C@@H](C(O)=O)c1ccc(O)cc1
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
http://aac.asm.org/
Structure-Activity Relationship of Carbacephalosporins and Cephalosporins: Antibacterial Activity and Interaction with the Intestinal Proton-Dependent Dipeptide Transport Carrier of Caco-2 Cells.
http://dissertations.ub.rug.nl/
....The substitution of the side chain of penG, phenyl acetic acid, with other side chains like D-phenylglycine and D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine, resulted in the semi-synthetic ��-lactam antibiotics ampicillin and amoxicillin (Figure 1), respectively, which are more stable and can be orally administered. Substitutions at C2 of the penicillin core resulted in new ��-lactam antibiotics to which resistant bacteria are sensitive.....
http://dissertations.ub.rug.nl/
A semi-random mutagenesis approach was followed to increase the performance of penicillin acylase PAS2 in the kinetically controlled synthesis of ampicillin from 6-aminopenicillanic acid (6-APA) and activated D-phenylglycine derivatives. We directed changes in amino acid residues to positions close to the active site that are expected to affect the catalytic performance of penicillin acylase: aR160, aF161, and bF24. From the resulting triple mutant gene bank, improved PAS2 mutants were recovered by only screening 700 active mutants with a HPLC-based screening method. A detailed kinetic analysis of the three most promising mutants, T23, TM33, and TM38, is presented. These mutants allowed the accumulation of ampicillin at 4 to 5 times higher concentrations than the wild-type enzyme, using D-phenylglycine methyl ester as the acyl donor. At the same time, the loss of activated acyl donor due to the competitive hydrolytic side reactions could be reduced to less than 20 % with the mutant enzymes compared to > 80 % with wild-type PAS2. Although catalytic activity dropped by a factor 5 to 10, the enhanced synthetic performance of the recovered penicillin acylase variants makes them interesting biocatalysts for the production of blactam antibiotics.
http://etds.ncl.edu.tw/
D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine (D-pHPG) is a D-amino acid which can be used to prepare semisynthetic antibiotics Amoxicillin. D-pHPG can be produced by two enzymatic steps. The substrate D-p-hydroxyphenylhydantoin (pHPH) is stereo-specifically hydrolysed by D-hydantoinase to the N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine(D-CpHPG). CpHPG can be further converted to D-pHPG by a second enzymatic step catalysed by an N-carbamyl-amino acid amidohydrolase.The bacterium Agrobacterium radiobacter can produce both D-hydantoinase and the N-carbamoyl-amino-acid amidohydrolase. The aim of this thesis is to develope an optimized complex medium for A. radiobacter and to evaluate pHPH and soy bean hydrolysate as inducers for the both enzymes. Fed-batch fermentation using a pre-determined feeding profiles was carried out for high cell density fermentation of A. radiobacter . The higest cell concentration obtained was 19.48g DCW/L with specific activity of 0.279 µmole/hr.mg cell . In order to reuse the D-hydantoinase and
amidohydrolase of the A. radiobacter cell a simple cell immobilization method was proposed. The cells suspension was floculated with PEI and further cross-linked with glutaraldehyde and chitosan After ten repeated batch reaction ,the immobilyed cell still can convert 4% (w/v)pHPH into D-pHPG with 58.5% conversion.
APPEARANCE
-156° ~ -160°
IRON
5ppm max
0.3% max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS (Globally Harmonised System) Classification: Skin irritation. Eye irritation. Specific target organ toxicity - single exposure. Hazard statements: Causes skin irritation. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation.
GHS
Danger
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36