PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
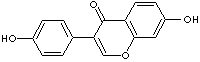
Oc1ccc2c(=O)c(c3ccc(O)cc3)coc2c1
CLASSIFICATION
Isoflavone, Non-Steroidal estrogen, Phytoestrogen, Protein Tyrosine Kinase (PTK) Inhibitor
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Soluble in DMSO
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Daidzein
Google Scholar Search - Daidzein
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Daidzein
PubChem Compound Summary - Daidzein
Drug Bank - Daidzein
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Daidzein
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Daidzein
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Daidzein
http://extension.agron.iastate.edu/
What are soy isoflavones? Isoflavones are biologically-active, nonnutritive compounds that are present in relatively large amounts in soybean and soyfoods. Soybeas contain two main types of isoflavones; daidzein and genistein. These compounds are part of a larger group of plant chemicals, called flavenoids, that are common in many fruits, vegetables, and legumes. Soybean are by far the most concentrated source of isoflavones in the human diet. Isoflavones are produced by the soybean plant as part of their defense mechanism against insects and diseases such as Phytophthora, and in response to environmental stresses such as drought. Isoflavones also play an important role in the growing soybean plant by stimulating nodule formation by nitrogen-fixing Rhizobium bacteria.
Local:
Daidzein is the genin of daidzin. They are abundant in soybeans. Daidzein is a
phytoestrogen suggested to play a role in preventing hormone-induced
cancers. Daidzein inhibits metabolic activation of benzo[a]pyrene and hydrogen
peroxide production in 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. It is known to be
useful to treat hypertension and menopausal syndrome as well as alcoholism.
Daidzein is a white crystalline powder; insoluble in water and chlorform,
slightly solube in alcohol. Chemical designation is 7-hydroxy-3-
(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H -1-benzopyran-4-one.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF FLAVONOID: Flavonoid is any member of a class of widely distributed biological natural products containing aromatic heterocyclic skeleton of flavan (2-Phenylbenzopyran) but no nitrogen in plants. Generally, flavonoids are biological pigments providing colours from red to blue in flowers, fruit and leaves. Besides their coloring in plants, flavonoids have important roles in the growth and development of plants; protection against UV-B radiation; forming antifungal barriers; antimicrobial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities; plant reproduction. Flavonoids also exhibit a wide range of biological properties including anti-microbial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities. Flavonoids are usually classified into main 6 subgroups as below plus flavans, neoflavonoids, flavonols, aurons, catechins according to the structural patterns.
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min
TOTAL IMPURITY
2.0% max
LOSS ON DRYING
1.0% max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May cause respiratory tract irritation. Causes eye and skin irritation. Target Organs: Eyes, skin.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319
P STATEMENTS
P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RIS PHRASES
36/38
SAFETY PHRASES
24-26