PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
Alternative to dicyclohexylcarbodiimide in peptide synthesis.
Coupling reagent for peptide syntheses
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
reacts to form 1,3-Diisopropylurea
log P
4.11 (octanol-water)
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
33 C
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
PubChem Compound Summary - N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide
http://www.bgu.ac.il/
Carbodiimide
reagents were designed to prevent the formation of the undesired
N-acylurea and to facilitate easy separation from the by-products.
The insolubility of the by-product occasionally caused problems
for the synthesis of polypeptides. Since the ureas from DIC and
CIC were relatively soluble in CH2Cl2, these reagents were more
suitable for solid-phase peptide synthesis than DCC. The solubilities
of N-cyclohexyl-N0-isopropylurea, N,N0-diisopropylurea, and N,N0-dicyclohexylurea
were 30, 5.2 and 1.5 g/L in CH2Cl2, respectively. In Fmoc solid-phase
peptide synthesis, the DIC/additive method was investigated in various
conditions by changing the additive, base,and solvent. Carpino demonstrated
that DIC/HOAt was superior to DIC/other additives.43 Further variations
of the carbodiimide such as BMC, BEC, and N,N0-dicyclopentylcarbodiimide
were reported (Fig. 12).44 Rapoport developed the hydrophilic side-chain-containing
carbodiimide, BDDC, in 1994. BDDC in THF, DMF, or toluene gave
a reasonable yield for the coupling reaction with a Bocprotected
amino acid and the by-product was easily removed by an acid wash.
http://www.peptide-and-dna.com/
The
formation of the amide bond together with chirality of the molecules
plays a key role in the preparation of a broad range of organic
compounds. It begins with the small molecules through the peptides
to fully synthetic proteins. Today, the synthesis of peptide or
protein based pharmaceutical drug requires up to 100 steps, the
name of the game is “production cost” and the modern synthetic
technologies play a central role in this battleA. thorough study
of the mechanism in each method involving basic producer for logistic
and technical support is a necessary term for the optimization of
the coupling step of a new peptide drug and further up-scaling towards
bulk manufacturing. Today, Cl-HOBt as an additive and HCTU/TCTU
are excellent alternatives to the most classic methods for the large
scale manufacturing of peptide and proteins.
Local:
Carbodiimides
are a group of organic compounds which have the resonance formula
N=C=N. Carbodiimides is formed by dehydration of urea or from thiourea.
Carbodiimides are readily reacts with various form of amines and
hydroxyl functional
groups. Carbodiimides are used as dehydration agents and
as activating agent of carboxylic acids to form esters or amides. The disubstituted
carboxyl activating agents are used for crosslinking
proteins to nucleic acids and formation of immunoconjugates
in peptide synthesis. N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)
is one of the most
common peptide coupling agents. It is a low melting point waxy solid; insoluble
in water but highly soluble in common organic solvents
like acetonitrile dichloromethane, dimethylformamide,
and tetrahydrofuran. DCC is a potent allergen. N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide
(DIC) is an alternative to DCC, DIC is a liquid and
is not an allergen. 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
(EDC) is a water-soluble
activating agent for amide bonding with primary amines. It also activates phosphate
groups. Typically, it is utilized in the pH
range 4.0-6.0 without buffers. In particular, amine and carboxylate buffers
should be avoided. Carbodiimides
are so active and cause racemization of the
amino acid. Active esters are
less reactive and less in danger of racemization. 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) and
1-hydroxy-7-aza-benzotriazole (HOAt)
are substances that react with the O-acylurea to form active esters.
HOAt is a condensation
additive in peptide synthesis. It
efficiently speeds up coupling process,
reduces the loss of chiral integrity, and
provides a visual indication (yellow to
colorless) of the reaction course. Other
active esters exit as non-nucleophilic anionic salts
of uronium or phosphonium
such as O-(Benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate(HBTU), O-(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate (HATU), (Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate
(PyBOP).
CARBODIIMIDES
|
Product |
CAS RN |
|
N,N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide |
538-75-0 |
| N,N'-Diphenylcarbodiimide | 622-16-2 |
|
N,N'-Di-tert-butylcarbodiimide |
691-24-7 |
|
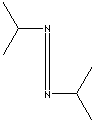
N,N'-Diisopropylcarbodiimide |
693-13-0 |
|
1,3-Di-p-tolylcarbodiimide |
726-42-1 |
| Bis(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)carbodiimide | 961-63-7 |
| Bis(trimethylsilyl)carbodiimide | 1000-70-0 |
| Bis(o-tolylcarbodiimide) | 1215-57-2 |
|
1-tert-Butyl-3-ethylcarbodiimide |
1433-27-8 |
|
N-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-N'-ethylcarbodiimide |
1892-57-5 |
| Bis(2,6-diisopropylphenyl)carbodiimide | 2162-74-5 |
| Bis(2,6-diethylphenyl)carbodiimide | 2162-75-6 |
|
N-Cyclohexyl-N'-(2-morpholinoethyl)carbodiimide metho-p-toluenesulfonate |
2491-17-0 |
| N-Cyclohexyl-N'-isopropylcarbodiimide | 3496-83-1 |
| N-Methyl-N'-phenylcarbodiimide | 4172-91-2 |
| 1-Cyclohexyl-3-(2-(4-morpholinyl)ethyl)carbodiimide | 15580-20-8 |
|
1-(3-(Dimethylamino)propyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide methiodide |
22572-40-3 |
| N,N'-Dicyclohexyl-N-methylcarbodiimidium iodide | 36049-77-1 |
| N-(2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidyl-1-oxyl) N'-(cyclohexyl)carbodiimide | 42249-40-1 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-(4-azonia-4,4-dimethylpentyl)carbodiimide | 45024-77-9 |
| Bis(2,4,6-triisopropyl-3-isocyanatophenyl)carbodiimide | 68083-39-6 |
| 1-Phenyl-3-trimethylaminopropyl carbodiimide | 79322-24-0 |
| N-Cyclohexyl-N'-(4-dimethylamino-alpha-naphthyl)carbodiimide | 86332-16-3 |
| N-Cyclohexyl-N'-(1-pyrenyl)carbodiimide | 98540-87-5 |
| 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminoethyl)carbodiimide | 141650-20-6 |
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Flammable liquid and vapor. Moisture sensitive. May be fatal if inhaled. May cause allergic respiratory and skin reaction. Causes severe eye irritation and possible injury. Causes skin and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Respiratory system, eyes, skin.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS




HAZARD STATEMENTS
H226-H315-H317-H318-H330-H334-H335
P STATEMENTS
P-210-P260-P280-P302+ P352-P310
![]() T+
Very toxic
T+
Very toxic
RISK PHRASES
10-26-37/38-41-42/43
SAFETY PHRASES
16-26-28-38-45