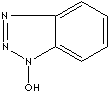
1-HYDROXYBENZOTRIAZOLE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
5 g/l at 30 C
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
Health hazard: 0, Fire: 0, Reactivity Hazard: 4
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - HOBt
PubChem Compound Summary - HOBt
http://www.arkat-usa.org/
Coupling
Additives: Ideally, peptide bond formation should be fast, quantitative
and carried out under mild conditions without affecting adjacent
stereogenic centers, without side reactions and with easily removable
side products. Although much progress has been achieved, some problems
still remain. A recent comprehensive review of all coupling reagents
and their acronyms is available. While the cyclization of homo-
or heterodetic peptides is not addressed directly in this report,
it is an important application of coupling reagents. In such cases,
it should be remembered that intramolecular cyclizations are best
carried out in highly diluted media (10-3 to 10-4 M) and as a result
the coupling reaction will be slow. Therefore, the activated intermediate
should not undergo unimolecular or solvent-induced decomposition.
The amino group is best protected as a carbamate and special conditions
may be needed for sterically hindered and N-methylated amino acids.
Tetramethyluronium derivatives have been reported to be used in
end-capping the amino group involved in the macrocyclization. Additives
are used in coupling reactions to inhibit side reactions and reduce
racemization. The rate of racemization of an alpha-amino acid derivative
depends on temperature, reaction conditions and its substituents.
A considerable increase in ease of racemization is also due to the
activating acyl substituent. An increase in acylating efficiency
(measured by the rate constant) is achieved by thermodynamic activation
of the acyl function and this activation increases the vulnerability
to racemization. Epimerization occurs as an activated acyl derivative
is formed or when it is reacted with the amino function.
Local:
Carbodiimides
are a group of organic compounds which have the resonance formula
N=C=N. Carbodiimide is formed by dehydration of urea or from thiourea.
Carbodiimides are readily reacts with various form of amines and
hydroxyl functional
groups. Carbodiimides are used as dehydration agents and
as activating agent of carboxylic acids to form esters or amides. The disubstituted
carboxyl activating agents are used for crosslinking
proteins to nucleic acids and formation of immunoconjugates
in peptide synthesis. N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC)
is one of the most
common peptide coupling agents. It is a low melting point waxy solid; insoluble
in water but highly soluble in common organic solvents
like acetonitrile dichloromethane, dimethylformamide,
and tetrahydrofuran. DCC is a potent allergen. N,N'-diisopropylcarbodiimide
(DIC) is an alternative to DCC, DIC is a liquid and
is not an allergen. 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
(EDC) is a water-soluble
activating agent for amide bonding with primary amines. It also activates phosphate
groups. Typically, it is utilized in the pH
range 4.0-6.0 without buffers. In particular, amine and carboxylate buffers
should be avoided. Carbodiimides
are so active and cause racemization of the
amino acid. Active esters are
less reactive and less in danger of racemization. 1-Hydroxybenzotriazole (HOBt) and
1-hydroxy-7-aza-benzotriazole (HOAt)
are substances that react with the O-acylurea to form active esters.
HOAt is a condensation
additive in peptide synthesis. It
efficiently speeds up coupling process,
reduces the loss of chiral integrity, and
provides a visual indication (yellow to
colorless) of the reaction course. Other
active esters exit as non-nucleophilic anionic salts
of uronium or phosphonium
such as O-(Benzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate(HBTU), O-(7-Azabenzotriazol-1-yl)-N,N,N',N'-tetramethyluronium
hexafluorophosphate (HATU), (Benzotriazol-1-yloxy)tripyrrolidinophosphonium hexafluorophosphate
(PyBOP).
|
|
APPEARANCE
PURITY (HPLC)
98.0% min
WATER
6.0 - 12.0% max
157 C min
APPEARANCE
PURITY (HPLC)
98.0% min
WATER
1.0% max
157 C min
Hazard OVERVIEW
Flammable solid
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H228 Causes serious eye irritation
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P210 Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. - No smoking.
![]() F
Highly Flammable
F
Highly Flammable
RISK PHRASES
5 Heating may cause an explosion
11 Highly Flammable
SAFETY PHRASES
15 Keep away from heat
16 Keep away from sources of ignition - No smoking
35
This material and its container must be disposed of in
a safe way
PRICE INFORMATION