| CAS
NO. |
943-73-7 |
|
| EINECS
NO. |
213-403-3 |
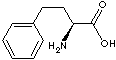
| FORMULA |
C6H5CH2CH2CH(NH2)COOH |
| MOL
WT. |
179.22 |
|
H.S.
CODE
|
2922.49 |
|
TOXICITY
|
|
| SYNONYMS |
(+)-2-Amino-4-phenylbutyric acid; L-HPA;
|
| (S)-alpha-Amino-benzenebutanoic acid;
(S)-(+)-2-Amino-4-phenylbutyric acid; |
| SMILES |
|
| CLASSIFICATION
|
|
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
|
| PHYSICAL
STATE |
white to
beige powder |
| MELTING POINT |
>
300 C |
| BOILING
POINT |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
|
| SOLUBILITY
IN WATER |
|
| pH |
|
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
AUTOIGNITION
|
|
|
NFPA
RATINGS
|
|
|
REFRACTIVE
INDEX
|
|
| FLASH
POINT |
|
| STABILITY |
Stable
under ordinary conditions |
|
APPLICATIONS
|
|
L-Homophenylalanine
is an intermediate for the synthesis of ACE-inhibitors (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor)
such as lisinopril to treat hypertension (high blood pressure and heart failure).
It is also used for the synthesis of NEPA
[(S,S)-N-(1-Ethoxycarbonyl-3-phenylpropyl)alanine]
which is a key intermediate to produce ACE-inhibitors
such as Enalapril, Delapril, Quinapril,
Ramipril. |
| SALES
SPECIFICATION |
|
APPEARANCE
|
Off-White crystalline powder |
|
ASSAY
(HPLC)
|
99.0%
min
|
|
OPTICAL
PURITY |
99.0% min
|
|
OPTICAL
ROTATION |
+45.5°
± 1° |
|
LOSS
ON DRYING |
0.5%
max |
| TRANSPORTATION |
| PACKING |
5kgs,
20kgs in can |
| HAZARD CLASS |
|
| UN
NO. |
|
| OTHER
INFORMATION |
|
In chemical, the prefix homo- indicates the addition of one methyl(CH2) group to
the main skeleton. Phenylalanine is an essential amino acid obtained in the levo form by hydrolysis
of proteins (as lactalbumin). Branched amino-acids (Valine, Isoleucine and Leucine ) with tryptophan
and phenylalanine (aromatic side chain amino acids) contribute to the structure
of protein by the tendency of its side chain composed only of carbon and
hydrogen to participate in hydrophobic interactions which determines the
tertiary structure of the peptide chain. In addition to its role in protein synthesis, it
is the metabolic precursor of the non-essential amino acid tyrosine which makes
hormones, such as norepinephrine and epinephrine in the normal body.
The prefix nor- describes
normal structure which has no branched chain of carbon atoms. But in case of
norepinephrine, it has one less methylene group than its homologue, epinephrine.
Phenylalanine is also converted to
phenylethylamine occuring naturally in the brain
to elevate mood. It is used to treat depression, inflammation, chronic pain,
Parkinson's disease. Phenylalanine is a key intermediate to make aspartame. |
