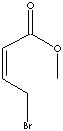
| Crotonic acid is a member of short and unsaturated cahin carboxylic acids;
trans-2-butenoic acid in IUPAC sysytem name and 3-methylacrylic acid in acrylic acid
series naming. It is a white to off-white crystals; soluble in water (the
solution is a weak acid); melting at 71 C; boiling at 185 C. It reacts violently
with bases, oxidants, reducing agents. It is found in croton oil used as a
standard irritant in pharmacological research; laxative and poisonous to human.
Tiglic acid is structurally the trans- form of methyl branched crotonic acid
found in croton oil (trans-2,3-Dimethylacrylic acid in acrylic acid
series naming). The cis- form of methyl branched crotonic acid is called
angelic acid obtainable naturally from roots of Angelica plant. They are
onoclinic poisonous crystals; soluble in hot water. They have a reactive double
bond and carboxylic group in one molecule. They can be used as co-monomers for polymerization to prepare
functional polymers as well as in protein sequencing and enzyme inhibiting.
Their derivatives, acyl halides, anhydrides, esters, amides and nitriles, are
used in making target products such as flavoring agents, internal
plasticizers, pesticides, dyes, textile treatment agents, fungicides, and
pharmaceuticals through further reactions of substitution, catalytic reduction, metal hydride reduction, diborane reduction,
keto formation with organometallic reagents, electrophile bonding at oxygen, and Claisen condensation on carboxylic group and electrophilic additions, reduction,
oxidation, radical additions, substitution and dienes formation on double bond.
|