PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
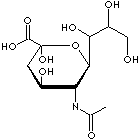
O1[C@H]([C@@H]([C@H](C[C@]1(C(O)=O)O)O)NC(C)=O)[C@H]([C@@H] (CO)O)O
CLASSIFICATION
Amino sugar, Sugar acid, Monosaccharide
EXTRA NOTES
Other CAS RN: 5977-25-3, 6225-16-7, 6918-20-3, 11032-36-3, 14752-56-8, 688025-48-1, 801157-24-4, 1195276-57-3, 1195521-74-4
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions. Hygroscopic.
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
USA.gov - Aceneuramic acid
Wikipedia Linking - Aceneuramic acid
Google Scholar Search - Aceneuramic acid
U.S. National Library of Medicine - Aceneuramic acid
PubChem Compound Summary - Aceneuramic acid
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Aceneuramic acid
EPA - Substance Registry Services - Aceneuramic acid
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
Biochem/physiol Actions: Both sialic acid and neuraminic acid are loosely used to refer to conjugates of neuraminic acid. N-Acetylneuraminic acid is often found as the terminal sugar of cell surface glycoproteins. Cell surface glycoproteins have important roles in cell recognition and interaction as well as in cell adhesion. Membrane glycoproteins are also important in tumor growth and metastases. Application: N-Acetylneuraminic acid (NANA, Neu5Ac) is a major component of glycoconjugates such as glycolipids, glycoproteins and proteoglycans (sialogylcoproteins) where it confers selective binding characteristics to the glycosylated component. Neu5Ac is used to study its biochemistry, metabolism and uptake in vivo and in vitro. Neu5Ac is used in the development of nanocarriers.
Local:
Neuraminic acid, C-9 amino sugar, is the aldol condensation compound of pyruvic acid and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine. Its nitrogen- and oxygen-substituted N-acyl derivatives called sialic acids are important in nature. Sialic acids are found as the terminal sugar of cell surface glycoproteins. They are widely distributed in bacteria and in animal tissue including blood cells. Sialic acids are components of lipids, polysaccharides, and mucoproteins, as cell surface glycoproteins that roles in cell adhesion, recognition, and interaction. N-Acetylneuraminic acid ( also called sialic acid or 'NANA' or 'SA' or Neu5Ac) is a white to off-white powder; melting point 185 - 187 C; soluble in water; insoluble in ether; unstable in strong acid and alkali. Ganglioside is any of a group of glycosphingolipids containing one or more sialic acids (N-acyl fatty acid derivative of sphingosine such as N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine, and N-acetylneuraminic acid) linked to a carbohydrate (glucose or galactose). The basic structure is ceramide-glucose-galactose-N-acetylneuraminic acid. Ganglioside is found in neuronal surface membran and spleen. It is a component the cell plasma membrane which modulates cell signal transduction activity. It is also considered to be involved in immunology. In the Svennerholm system abbrevations, gangliosides are designated G for ganglioside, plus subscript M, D, or T for mono-, di-, or trisialo, respectively, the subscript letter being followed by a subscript arabic numeral to indicated sequence of migration in thin-layer chromatograms. The main gangliosides of the brain are GM1, GD1a, GD1b and GT1. GM3 is present mainly outside brain tissues. Natural and semisynthetic gangliosides are considered possible therapeutics for neurodegenerative disorders.
|
|
APPEARANCE
PURITY (G.C.)
98.0% min
OPTICAL ROTATION
-30° ~ -34°
PRICE INFORMATION