PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
|
|
|
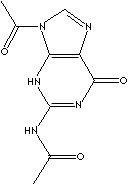
| N2,9-DIACETYLGUANINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 3056-33-5 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 221-287-0 | |
| FORMULA | C9H9N5O3 | |
| MOL WT. | 235.20 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
||
|
TOXICITY |
|
|
| SYNONYMS | N,9-Diacetylguanine; | |
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | white to off-white powder | |
| MELTING POINT | > 250 C | |
| BOILING POINT | ||
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY | ||
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | ||
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION |
|
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 1; Flammability: 0; Instability: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT | ||
| STABILITY |
Stable under ordinary conditions |
|
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION AND APPLICATIONS |
||
| Purine is a heterocyclic compound featured by a fused pyrimidine and imidazole rings composed of carbon and nitrogen atoms. The simplest one is purine itself and the two major purines are adenine(6-Aminopurine) and guanine(2-Amino-6-hydroxypurine). Other important purines are caffeine, uric acid, theobromine, and theophylline. Purine and its derivatives are biologically important components of nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and coenzymes. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
white to off-white powder | |
|
ASSAY |
98.0% min | |
| MELTING POINT | > 250 C | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | Not regulated | |
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: , Risk Phrases: 22-36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-37/39 | ||
|
|
|