PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
480-41-1 (S-form)
207-550-2
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
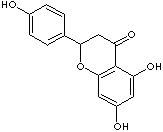
c12c(O[C@@H](c3ccc(O)cc3)CC1=O)cc(O)cc2O
CLASSIFICATION
Anti-ulcer, Estrogen antagonist, Gastrointestinal agent, Resorcinol
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
247 - 250 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking - Naringenin
Google Scholar Search - Naringenin
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Naringenin
PubChem Compound Summary - Naringenin
Drug Bank - Naringenin
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Naringenin
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Naringenin
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Naringenin
Human Metabolome Database - Naringenin
http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/
Hazardous
Substances Data Bank - Naringenin
http://ajpgi.physiology.org/
Naringenin, the predominant flavanone in grapefruit, mainly occurs as glycosides such as naringenin-7- rhamnoglucoside or naringenin-7-glucoside. This study compared kinetics of absorption of naringenin and its glycosides in rats either after a single flavanone-containing meal or after adaptation to a diet for 14 days. Regardless of the diet, circulating metabolites were glucurono- and sulfoconjugated derivatives of naringenin. The kinetics of absorption of naringenin and naringenin-7-glucoside were similar, whereas naringenin-7-rhamnoglucoside exhibited a delay in its intestinal absorption, resulting in decreased bioavailability. After naringenin-7-glucoside feeding, no glucoside was found in the cecum. However, after feeding naringenin-7-rhamnoglucoside,
Local:
Naringenin is a flavonone that
is considered to have a bioactive effect on human health
as antioxidant, radical scavenger, antiinflammatory, carbohydrate metabolism promoter, immunity
system modulater. It works as an anti-ulcer agent and estrogen antagonist
which inhibit the action or biosynthesis of
estrogenic compounds. Naringin is the aglycones of naringenin. Naringin is known
as an antioxidant in the body. in biology, antioxidants act to protect cells against free radicals. Free
radicals play an important role in a number of biological processes such as the
intracellular killing of bacteria by neutrophil granulocytes and certain cell
signaling processes. However, because of their reactivity, free radicals can
cause side reactions resulting in cell damage, which may contribute to the
development of cardiovascular disease and cancer. Lipids, protein and nucleic
acids are weak to free radicals. Free radicals may be involved in the mechanisms
of aging itself also. The body has a number of mechanisms to minimize free
radical induced damage and to repair damage. Antioxidant enzymes produced in
the body play a key role in these defense mechanisms, such as glutathione
peroxidase, glutathione reductase, catalase, thioredoxin reductase and
superoxide dismutase. Additionally, chemical antioxidants neutralize free
radicals by accepting or donating an electron to eliminate the unpaired
condition. These antioxidants include three vitamins (vitamin A, vitamin C and
vitamin E), polyphenols, bilirubin and uric acid. Synthetic or natural
antioxidants are widely used in nutrition and medicine and prepared foods for
the effect to slow down the natural aging process and to prevent or delay
certain diseases that result from cellular damage. But there should be
considerable researches whether antioxidant supplementation provide beneficial
effect, and if so, which and what amount of antioxidants are optimal. There are
hundreds of different types of nutritional antioxidants include vitamins,
coenzymes, selenium, minerals, hormones, carotenoids, non-carotenoid terpenoids,
flavonoids (flavonols, flavones isoflavones, flavanols,, anthocyanidins),
nonflavonoid phenolics, polyphenolics and their esters (ellagic acids, citric
acids, uric acids, gallic acids, salicylic acids, rosmarinic acids, cinnamic
acids, chlorogenic acids, chicoric acids). Some naringenin
molecules include:
|
Product |
CAS RN |
| Phlorhizin | 60-81-1 |
| Phloretin | 60-82-2 |
| Carthamidin | 479-54-9 |
| Naringenin | 480-41-1 |
| 4'-Methylnaringenin | 480-43-3 |
| Pectolinarigenin | 520-12-7 |
|
Prunin |
529-55-5 |
|
Sakuranetin |
2957-21-3 |
| Naringenin-6-C-glucoside | 3682-03-9 |
| Naringin | 10236-47-2 |
| Narirutin | 14259-46-2 |
|
Didymin |
14259-47-3 |
|
Poncirin |
14941-08-3 |
|
Naringin dihydrochalcone |
18916-17-1 |
|
Naringenin 4',7-dimethyl ether |
29424-96-2 |
| Naringenin chalcone | 73692-50-9 |
| 3'-Prenylnaringenin | 119240-82-3 |
Flavonoid is any member of a class of widely distributed biological natural products containing aromatic heterocyclic skeleton of flavan (2-Phenylbenzopyran) but no nitrogen in plants. Generally, flavonoids are biological pigments providing colours from red to blue in flowers, fruit and leaves. Besides their coloring in plants, flavonoids have important roles in the growth and development of plants; protection against UV-B radiation; forming antifungal barriers; antimicrobial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities; plant reproduction. Flavonoids also exhibit a wide range of biological properties including anti-microbial, insecticidal and oestrogenic activities. Flavonoids are usually classified into main 6 subgroups as below plus flavans, neoflavonoids, flavonols, aurons, catechins according to the structural patterns.
- Flavonols (Hydroxy derivatives of flavone): Fisetin, Galangin, Kaempferide, Kaempferol, Morin, Myricetin, Myricitrin, Quercetin, Quercetrin, Rhamnetin, Robinin, Rutin, Spirenoside
- Flavones (skeleton: 2-phenylchromen-4-one): Apigenin, Baicalein, Chrysin, Diosmetin, Diosmin, Flavone, Luteolin, Rpoifolin,Tangeretin, Techtochrysin, Rhamnazin, Nobiletin, Natsudaidain.
- Isoflavones (skeleton: 3-phenylchromen-4-one): Daidzin, Genistein, Irilone, Luteone, Prunetin, Pratensein,
- Flavonones (derivation by reduction of the 2(3) C=C bond): Eriodictyol, Hesperidin, Hesperetin, Likvirtin, Naringin; Naringenin; Pinocembrin
- Flavanols (derivation by reduction of the keto group):(+)-Catechin, (+)-Gallocatechin, (-)-Epicatechin (EC), (-)-Epigallocatechin (EGC), (-)-Epicatechin 3-gallate (ECG), (-)-Epigallocatechin 3-gallate (EGCG), Theaflavin, Theaflavin 3-gallate, Theaflavin 3'-gallate, Theaflavin 3,3' digallate, Thearubigins
- Anthocyanidins (aglycones of the glycoside anthocyanins): Apigeninidin, Cyanidin, Delphinidin, Diosmetinidin, Guibourtinidin, Fisetinidin, Luteolinidin, Malvidin, Pelargonidin, Peonidin, Robinetinidin, Tricetinidin, Capensinidin, Petunidin, Europinidin, Aurentinidin, Columnidin, 5-Desoxy-malvidin, 5-Desoxy-peonidin, Hirsutinidin, Rosinidin
APPEARANCE
ASSAY
98.0% min
LOSS ON DRYING
5% max
ASH
5% max
HEAVY METALS
10ppm max
ARSENIC (As)
2ppm max
MERCURY(Hg)
ippm max
LEAD (Pb)
2ppm max
PESTICIDE RESIDUES
2ppm max
MICROBIOLOGICAL TEST
Total Plate Count:10000cfu/g max
Yeast & Mold:1000cfu/g max
E.Coli:Negative
Salmonella:Negative
Staph Aureus:Negative
Pseudomonas aeruginosa:Negative
PARTICLE SIZE
100 mesh
GMO STATUS
GMO Free
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Causes eye, skin, and respiratory tract irritation. Target Organs: Respiratory system, eyes, skin.
GHS
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H319-H335
P STATEMENTS
P261-P305 + P351 + P338
![]()
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36