PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Wikipedia Linking: http://en.wikipedia.org/
Google Scholar Search: http://scholar.google.co.kr/
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Oxaliplatin, a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent with a 1,2-diaminocyclohexane (DACH) carrier ligand, has shown in vitro and in vivo efficacy against many tumor cell lines, including some that are resistant to cisplatin and carboplatin. The retention of the bulky DACH ring by activated
oxaliplatin is thought to result in the formation of platinum-DNA adducts, which appear to be more effective t blocking DNA replication and are more cytotoxic than adducts formed from cisplatin. Studies by the National Cancer Institute (NCI) have suggested that oxaliplatin has a spectrum of activity different from that of either cisplatin or carboplatin, suggesting that it has different molecular targets and/or mechanisms of resistance. Oxaliplatin has been demonstrated to differ in some mechanisms associated with the development of cisplatin resistance. Compared with cisplatin-conditioned cells, deficiencies in mismatch repair (MMR) and increases in replicative bypass, which appear to contribute to cisplatin resistance, have not been shown to induce a similar resistance to oxaliplatin. A decreased likelihood of resistance development makes oxaliplatin a good candidate for first-line therapy. Studies also demonstrate additive and/or synergistic activity with a number of other compounds, however, suggesting the possible use of oxaliplatin in combination therapies.
http://www.drugbank.ca/
Oxaliplatin is a platinum-based chemotherapy drug in the same family as cisplatin and carboplatin. It is typically administered in combination with fluorouracil and leucovorin in a combination known as Folfox for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Compared to cisplatin the two amine groups are replaced by cyclohexyldiamine for improved antitumour activity. The chlorine ligands are replaced by the oxalato bidentate derived from oxalic acid in order to improve water solubility. Oxaliplatin is marketed by Sanofi-Aventis under the trademark Eloxatin®.
http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/
...While DNA damage is a key factor in the development and evolution of cancer cells, continued damage is used as part of clinical treatments for cancer, forcing malignant cells into apoptosis or senescence. Many chemotheraputic drugs such as bleomycin, mitomycin, and cisplatin, are effective because they cause further DNA damage in cancer cells that replicate at a faster rate than surrounding tissue. Cellular DNA repair mechanisms are a doubleedged sword; by reducing mutations that may lead to cancer, these processes strive for genomic integrity, but the same mechanisms in malignant cells allow those cells to survive additional DNA damage and continue uncontrolled growth. In order to block this survival mechanism within cancer cells, clinical trials are now being performed using inhibitors to specific DNA repair enzymes, including MGMT, PARP, and DNA-PK.
Local
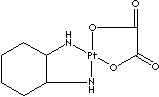
Carboplatin, a platinum coordination compound which contains a platinum atom surrounded with two ammonia groups and two other ligands in a ring structure. Cisplatin is an analogue which has two chloride atoms instead of ring structure. Oxaliplatin contains a platinum atom complexed with 1,2-diaminocyclohexane and with an oxalate ligand as a leaving group. It is known that diaminocyclohexane group contributes greater cytotoxicity than cisplatin and carboplatin. Oxaliplatin is not generally cross-resistant to cisplatin or carboplatin. They are capable of forming platinum complexes producing inter- and intrastrand DNA crosslinks with neighboring guanine residues, resulting in DNA-mismatch repair (MMR) activity in the cancer cells. Carboplatin has less nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, ototoxicity and emetogenesis and more stability than cisplatin. They, platinum-based antineoplastics, have a broad spectrum of antitumor activity in the treatments of carcinomas of ovarian, testicular, bladder, small and non–small cell lung, head and neck carcinoma, and seminoma. They are synergistic with fluorouracil. They are radiation sensitive. The chemical designation of cisplatin is (SP-4-2)-diaminedichloroplatinum (II). It is a yellow crystalline powder; soluble in water and saline; administered intravenously. The chemical designation of carboplatin is (SP-4-2)-diammine [1,1-cyclobutanedicarboxylato (2-)-0, 0']- platinum (II). It is a white crystalline powder; soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol, acetone, and dimethylacetamide; administered intravenously. The chemical designation of oxaliplatin is SP-4-2-(1R-trans))- (1,2-cyclohexanediamine-N,N')- (ethanedioato(2-)-O,O') platinum (II). It is a white crystalline powder; soluble in water; very slightly soluble in methanol; insoluble in ethanol, hexane, benzene and acetone.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies Test A,B
ASSAY
98.0 - 102.0% (HPLC)
PLATINUM CONTENT
48.0 - 50.0%
RELATED SUBSTANCE
Complies
WATER
1.0% max
SPECIFIC ROTATION
+73° ~ +78°
pH
5.0 - 7.0
CLARITY
Complies
SILVER
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ALKYLATING AGENTS AS ANTITUMOR
- Nitrogen mustard
- Chlorambucil (CAS RN: 305-03-3)
- Mechlorethamine (CAS RN: 51-75-2)
- Melphalan (CAS RN:148-82-3)
- Uracil Mustard (CAS RN: 66-75-1)
- Cyclophosphamide (CAS RN: 50-18-0)
- Iphosphamide (CAS RN: 3778-73-2)
- Nitrosoureas
- Triethylenemelamine (CAS RN: 51-18-3)
- Hexamethylmelamine (CAS RN: 645-05-6)
- Bis-chloroethylnitrosourea (CAS RN: 154-93-8)
- Chloroethylcyclohexylnitrosourea (CAS RN: 13010-47-4)
- Streptozotocin (CAS RN: 18883-66-4)
- Platinum compounds
- Carboplatin (CAS RN: 41575-94-4)
- Oxaliplatin (CAS RN: 61825-94-3)
- Cisplatin (CAS CN: 15663-27-)
- Tetraplatin (CAS RN: 62816-98-2)
- (Carboxyphthalato)platinum (CAS RN: 65296-81-3)
- Alkyl sulfonates
- Busulfan (CAS RN: 55-98-1)
- Mannosulfan (CAS RN: 7518-35-6)
- Treosulfan (CAS RN: 299-75-2)
- Aziridines
- Thiotepa (CAS RN: 52-24-4)
HAZARD OVERVIEW
Causes skin irritation. May cause an allergic skin reaction. Causes serious eye irritation. May cause respiratory irritation. Suspected of causing cancer. Target Organ Effect, Skin sensitiser, Irritant. Target Organs:Liver injury may occur., Kidney, ears, Blood, Peripheral nervous system., Bone marrow, Testes., Female reproductive system.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS


HAZARD STATEMENTS
H315-H317-H319-H335-H351
P STATEMENTS
P261-P280-P305 + P351 + P33
![]() Xn
Xn
RISK PHRASES
36/37/38-40-42/43
SAFETY PHRASES
26-36