| PHENOTHIAZINE | ||
|
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION |
||
| CAS NO. | 92-84-2 |
|
| EINECS NO. | 202-196-5 | |
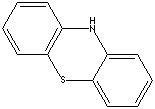
| FORMULA | C12H9NS | |
| MOL WT. | 199.28 | |
|
H.S. CODE |
2934.30 | |
|
TOXICITY |
||
| SYNONYMS | Dibenzo-p-thiazine; Dibenzothiazine; | |
| 10H-Phenothiazine; Dibenzo-1,4-thiazine; Biverm; Contaverm; Contavern; contraverm; Feeno; Fenoverm; Fentiazine; Helmetine; helmetina; Lethelmin; Nemazene; nemazine; Orimon; Padophene; phenegic; phenosan; phenothiazone; Phenovarm; phenoverm; phenovis; phenoxur; phenthiazine; Souframine; Thiodiphenylamine; Vermitin; | ||
| SMILES |
|
|
|
CLASSIFICATION |
||
|
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES |
||
| PHYSICAL STATE | light yellow crystals | |
| MELTING POINT | 183 - 186 C | |
| BOILING POINT |
235 C |
|
| SPECIFIC GRAVITY |
1.34 |
|
| SOLUBILITY IN WATER | Insoluble | |
| pH | 7 (10% Aq. Sol) | |
| VAPOR DENSITY |
|
|
|
AUTOIGNITION |
470 C |
|
|
NFPA RATINGS |
Health: 2; Flammability: 2; Instability: 0 | |
|
REFRACTIVE INDEX |
|
|
| FLASH POINT |
202 C |
|
| STABILITY | Stable under ordinary conditions | |
|
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS |
||
| Phenothiazine, also called dibenzothiazine or thiodiphenylamine is a yellow or green crystalline compound soluble in hot acetic acid, benzene, and ether. It is a three-ring structure compound in which two benzene rings are joined by a sulfur and nitrogen atom at nonadjacent positions. It is obtained from by fusing diphenylamine with sulfur. Generally phenothiazine structure compounds are known as active adrenergic blocking agents. They are used in pharmaceutical manufacturing especially antipsychotic drugs. Phenothiazine and its derivatives are used in as worming agents (anthelmintic) in veterinary medicine effective against a wide range of parasitic insects in animals which provides food for human. (it is a highly toxic drug which is not recommended for human use directly). Phenothiazine is also used as a stabilizer against polymerization of acrylates. | ||
| SALES SPECIFICATION | ||
|
APPEARANCE |
light yellow crystals | |
|
ASSAY |
97.0% min |
|
| MELTING POINT | 183 - 186 C | |
| LOSS ON DRYING | 0.2% max | |
| TRANSPORTATION | ||
| PACKING |
25kgs
in fiber drum
|
|
| HAZARD CLASS | ||
| UN NO. | ||
| OTHER INFORMATION | ||
| Hazard Symbols: XI, Risk Phrases: 36/37/38, Safety Phrases: 26-37/39 | ||
| GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS |
||
The term antipsychotic refers to a group of drugs effective in the treatment of
psychosis including schizophrenic, paranoid, schizoaffective, bipolar disorder,
and other psychotic disorders. Traditional antipsychotic agents have
phenothiazine structure chemically. Phenothiazinene drugs are adrenergic
blocking agents. Their pharmacologic actions including central nervous system
depression, prolongation and potentiation of the effects of narcotic and
hypnotic drugs, hypotensive activity, and antispasmodic, antihistaminic, and
antiemetic activity. Other chemcial structures for antipsychotic drugs are
diverse, they include thioxanthene, butyrophenone, dibenzoxazepine,
dihydroindolone, benzisoxazole, and diphenylbutylpiperidine. Antipsychotic
agents bind to dopamine, histamine, muscarinic cholinergic, a-adrenergic, and
serotonin receptors. Blockade of dopaminergic transmission in various areas is known
to be responsible for their major effects such as not
only antipsychotic action by
blockade in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas and and antiemetic effects by blockade in the chemoreceptor trigger
zone of the medulla but also extrapyramidal side effects
(dystonia, akathisia, parkinsonism, and tardive dyskinesia) by blockade in the
basal ganglia and sedation and autonomic side effects (orthostatic
hypotension, blurred vision, dry mouth, nasal congestion, and constipation) by blockade of histamine, cholinergic, and adrenergic receptors.
The antipsychotic agents may be divided by chemical group and and the decreased propensity of extrapyramidal side effects
into two main groups and a new class which is being
processed.
|
||