PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & APPLICATIONS
Anthelmintic (also spelled anthelminthic) is a chemical substance used to expel or destroy tapeworms in domestic animals. Some common anthelmintic active ingredients classified by chemical structure include;
- Benzimidazoles
- Albendazole (CAS #: 54965-21-8)
- Fenbendazole (CAS #: 43210-67-9)
- Mebendazole (CAS #: 31431-39-7)
- Oxfendazole (CAS #: 53716-50-0)
- Oxibendazole ((CAS #: 20559-55-1)
- Triclabendazole (CAS #: 68786-66-3)
- Diphenylsulfides
- Bithionol (CAS #:97-18-7)
- Febantel (CAS #: 58306-30-2)
- Hexahydropyrazines
- Diethylcarbamazine (CAS #: 90-89-1)
- Piperazine (CAS #: 110-85-0)
- Praziquantel (CAS #: 55268-74-1)
- Imidazothiazoles
- Levamisole (CAS #: 14769-73-4)
- Tetramisol (CAS #: 5036-02-2)
- Macrocylic Lactones
- Abamectin (CAS #: 71751-41-2)
- Doramectin (CAS #: 117704-25-3)
- Eprinomectin (CAS #: 123997-26-2)
- Eprinomectin B1a (CAS#: 133305-88-1)
- Eprinomectin B1b (CAS #: 133305-89-2)
- Ivermectin (CAS #: 70288-86-7)
- Ivermectin B1a (CAS #: 70161-11-4)
- Ivermectin B1b (CAS #: 70209-81-3)
- Moxidectin (CAS #: 113507-06-5)
- Salicylanilide
- Closantel (CAS #: 57808-65-8)
- Niclosamide Base (CAS #: 50-65-7)
- Niclosamide Monohydrate (CAS #: 7336-56-2)
- Niclosamide Ethanolamine salt (CAS #: 1420-04-8)
- Niclosamide Piperazine salt (CAS #: 34892-17-6)
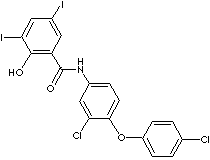
- Oxyclozanide (CAS #: 2277-92-1)
- Rafoxanide (CAS #: 22662-39-1)
- Tetrahydropyrimidines
- Morantel (CAS #: 20574-50-9)
- Pytrantel Pamoate (CAS #: 22204-24-6)
- Others
- Clorsulon (CAS #: 60200-06-8)
- Nitroxinil (CAS #: 1689-89-0)
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies Test A, B
ASSAY
98.0 - 102.0%
CHLORIDE
0.25% max
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
SULFATED ASH
0.1% max
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF SALICYLANILIDE
- Dibromsalan (CAS #: 87-12-7): 4',5-Dibromosalicylanilide
- Metabromsalan (CAS #: 2577-72-2): 3,5-Dibromosalicylanilide
- Tribromsalan (CAS #: 87-10-5): 3,4',5-Tribromosalicylanilide
Some salicylanilide derivatives are used as aromatic amide pesticides and anthelmintics.