PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
CLASSIFICATION
Psychotropic, Tranquilizing agent, Atypical antipsychotic, Dopamine antagonist, Serotonin antagonistBenzisoxazole, Piperidine, Lactam
EXTRA NOTES
A selective blocker of DOPAMINE D2 RECEPTORS and SEROTONIN 5-HT2 RECEPTORS that acts as an atypical antipsychotic agent. It has been shown to improve both positive and negative symptoms in the treatment of SCHIZOPHRENIA.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
REFRACTIVE INDEX
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Risperidone
PubChem Compound Summary - Risperidone
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
Risperidone
compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and
in vivo receptor binding
http://www.bcc-asa.org/
Risperidone
Treatment of Autistic Disorder: Longer-Term Benefits and Blinded
Discontinuation After 6 Months
http://www.choiceandmedication.org/
What
is risperidone?:Risperidone (sometimes also known by its trade name
Risperdal®) is usually used to help treat the symptoms of psychosis,
schizophrenia and mania, and to prevent these symptoms coming back.
It is often also used to help the symptoms of ADHD and bipolar mood
disorder. It is one of a group of medicines called antipsychotics
or neuroleptics. It is made as tablets, melt-in-the-mouth tablets,
a syrup and a long-acting injection.
Local:
Antihistamine is a group of drugs characterized by the ability to block the
action of histamines on H1 receptors. The principal use is to treat allergies,
hives, and other local and systemic hypersensitivity reactions. Some
antihistamines can also be used in the control of insomnia, motion sickness, or
vertigo. First-generation antihistamines can cause side effect of sedation.
Second-generation antihistamines (fexofenadine, loratadine) are nonsedating.
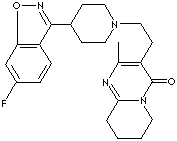
Risperidone, a benzisoxazole derivative compound, is used as an antipsychotic
agent for the therapy in schizophrenia and other related psychotic disorders. It
is a white to off-white powder; insoluble in water, soluble in methylene
chloride, methanol and dilute acid. Its chemical designation is
3-(2-(4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1- piperidinyl)ethyl)-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-
methyl-4H-pyrido [1,2-a] pyrimidin-4-one.
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
Complies ( IR spectrum)
ASSAY (HPLC)
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
20ppm max
SOLVENT RESIDUE
0.5% max
6.1 (Packing group: III)
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF ANTIPSYCHOTIC AGENTS
- Typical Antipsychotic
- Chlorpromazine (CAS #: 50-53-3, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Promazine (CAS #: 58-40-2, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Triflupromazine (CAS #: 146-54-3, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Methotrimeprazine (CAS #: 60-99-1, Phenothiazine with aliphatic side chain)
- Thioridazine (CAS #: 50-52-2, Phenothiazine with piperidine side chain)
- Mesoridazine (CAS #: 5588-33-0, Phenothiazine with piperidine side chain)
- Acetophenazine (CAS #:2751-68-0, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Perphenazine (CAS #: 58-39-9, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Trifluoperazine (CAS #: 117-89-5, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Fluphenazine (CAS #: 69-23-8, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Prochlorperazine (CAS #: 58-38-8, Phenothiazine with piperazine side chain)
- Chlorprothixene (CAS #: 113-59-7 Thioxanthene)
- Thiothixene (CAS #: 22189-31-7, Thioxanthene)
- Haloperidol (CAS #: 52-86-8, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Pimozide (CAS #: 2062-78-4, Phenylbutylpiperadine)
- Loxapine (CAS #: 1977-10-2, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Molindone (CAS #: 7416-34-4, Dihydroindolone)
- Atypical Antipsychotics
- Clozapine (CAS #: 5786-21-0, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Olanzapine (CAS #: 132539-06-1, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Quetiapine (CAS #: 111974-69-7, Dibenzoxazepine)
- Ziprasidone (CAS #: 138982-67-9, Benzisoxazole)
- Risperidone (CAS #: 106266-06-2, Benzisoxazole)
- Partial dopamine agonists
- Aripiprazole (CAS #: 129722-12-9, Dihydroquinolinone)
- Lithium carbonate
GHS
OSHA Hazards: Toxic by ingestion
Danger
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H301 Toxic if swallowed.
PRECAUTIONARY STATEMENTS
P301 + P310 IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician.
![]() T
Toxic
T
Toxic
RISK PHRASES
25 Toxic if swallowed
SAFETY PHRASES
28
After contact with skin, wash immediately with plenty
of ... (to be specified by the manufacturer)
36
Wear suitable protective clothing
45
In case of accident or if you feel unwell, seek medical
advice immediately (show label where possible)