BETULIN
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
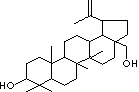
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Lup-20(29)-ene-3beta,28-diol; Messagenin; Triterpenoid; Betulinic alcohol;
CLASSIFICATION
Triterpene
EXTRA NOTES
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
AUTOIGNITION
NFPA RATINGS
Health hazard: 2, Flammability: 0, Physical hazards: 0
REFRACTIVE INDEX
Stable under ordinary conditions
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Betulin is a constituent of the cork layer of the outer bark of Betula alba, B. pendula, B. pubescent and B. platyphylla. Other sources are Diospyros leucomelas, Nelumbo nucifera, Zizyphus mauritiana and seeds of Ziziphus vulgaris var. spinosus. Betulin also occurs as the palmitate in the glue firm bark of Trochodendron aralioides.The antiphlogistic activity of betulin was confirmed in various experimental models. Studies on the activity of a methanolic extract from the rhizomes of N. nucifera, as well as betulin and betulinic acid revealed a marked inhibition of the carrageenin- and serotonin-induced rat paw edema, which was comparable to that of the standard anti-inflammatory agents phenylbutazone and dexamethazone. The authors of these studies concluded that lupane derivatives (steroid triterpenes), have an affinity for glucocorticoid receptors. This mechanism of action was confirmed by another study on three triterpenes isolated from D. leucomelas: betulin, betulic acid (Recio et al. 1995) oleanolic (Singh et al. 1992) and ursolic acid (Najid et al. 1992). All triterpenes tested showed anti-inflammatory activity in the following model tests: serotonin -, cararrageenan-induced paw edema; and TPA- and EPP-induced eye edema. Administration of progesterone, actinomycine D and cycloheximide helped to clarify a glucocorticoidal mechanism of action for the compounds tested, and among which betulinic acid showed the highest activity (Recio et al. 1995). (http://www.zsf.jcu.cz/)
Betulinic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene. It has several botanical sources, but can also be chemically derived from betulin, a substance found in abundance in the outer bark of white birch trees (Betula alba). Betulinic acid has been found to selectively kill human melanoma cells while leaving healthy cells alive. For the past four decades, the incidence of melanoma has been increasing at a higher rate than any other type of cancer source:http://biotech.icmb.utexas.edu/)Betulinic acid, a pentacyclic triterpene, is known to have inhibitory property for aminopeptidase N (EC 3.4.11.2) activity and thus is a potential anti-melanoma agent by selectively killing human melanoma cells. It is a chemical compounds that may assist in fighting oral bacteria which would promote tooth decay. It is also considered to have effective as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, antimalarial, and prostaglandin antagonist.
- Analgesic
- Anti-HIV Agent
- Anti-infective Agent
- Anti-inflammatory Agent
- Antimalarial
- Antineoplastic Agent
- Antiparasitic Agent
- Antiprotozoal Agent
- Antiretroviral Agent
- Antirheumatic Agent
- Antiviral Agent
- Hormone Antagonist
- Peripheral Nervous System Agent
- Prostaglandin antagonist
- Sensory System Agent
APPEARANCE
ASSAY (G.C)
98.0% min
OPTICAL ROTATION
HAZARD OVERVIEW
May be harmful if swallowed. Causes mild skin irritation. Causes damage to organs. Toxic if inhaled. Causes respiratory tract irritation. Toxic if absorbed through skin. Causes skin irritation. Causes eye irritation. Toxic if swallowed.
GHS
Warning
PICTOGRAMS

HAZARD STATEMENTS
H303-H316-H370
P STATEMENTS
P260-P307 + P311
![]() Xn
Xn
RISK PHRASES
20/21/22-68/20/21/22
SAFETY PHRASES
36/37