FELBAMATE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
25451-15-4
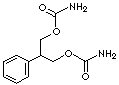
C11H14N2O4
TOXICITY
H.S. CODE
Felbamate; 2-Phenyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate;
Felbamato; Felbamatum; Felbatol;
C(c1ccccc1)(COC(=O)N)COC(=O)N
CLASSIFICATION
Anticonvulsant, Antioxidant, Antiepileptic,
EXTRA NOTES
An orphan drug used as therapy for the treatment of partial and generalized seizures.
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
150 ~ 154 C
REFRACTIVE INDEX
NFPA RATINGS
Health hazard: 1, Flammability: 0, Physical hazards: 0
AUTOIGNITION
FLASH POINT
EXTERNAL LINKS & GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Drug Information Portal (U.S. National Library of Medicine) - Felbamate
PubChem Compound Summary - Felbamate
Drug Bank - Felbamate
KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) - Felbamate
http://www.ebi.ac.uk/ - Felbamate
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ - Felbamate
http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/Felbamate and meprobamate are structurally related propanediol dicarbamates that possess distinct pharmacological profiles. Felbamate is a minimally sedative, broad-spectrum anticonvulsant, whereas meprobamate is a strong sedative-anxiolytic agent. Previously, we reported that felbamate potentiates γ-aminobutyric acidA(GABAA) receptor Cl− currents and inhibits N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor currents. Here we further characterized the interaction of the two dicarbamates with GABAA receptors to determine the basis for their pharmacological differences. In whole-cell voltage-clamp recordings from cultured rat hippocampal neurons, meprobamate enhanced GABA-evoked responses in a concentration-dependent manner and, at high concentrations (>1 mM), exhibited a separate channel-blocking effect that limited the magnitude of GABAA receptor potentiation. At equivalent concentrations, meprobamate produced substantially greater potentiation than did felbamate. Furthermore, meprobamate (but not felbamate), in the absence of GABA, directly activated Cl− currents that could be attenuated by the GABAA receptor antagonists bicuculline and picrotoxin. The mean deactivation time constant of whole-cell currents evoked by 10 mM meprobamate (110 ms) or 1 and 3 μM GABA (180 ms) were faster than the deactivation time constant of 10 mM meprobamate (490 ms) or 3 mM felbamate (470 ms) in the presence of GABA. Meprobamate and felbamate prolonged the mean burst duration of GABA-activated unitary currents in excised outside-out membrane patches. In addition, at high (supratherapeutic) concentrations, meprobamate blocked NMDA-activated currents. We conclude that felbamate and meprobamate have barbiturate-like modulatory actions on GABAA receptors, but meprobamate has greater activity and, unlike felbamate, is able to directly activate the receptor.
http://www.aafp.org/
Newer Antiepileptic Drugs: Gabapentin, Lamotrigine, Felbamate, Topiramate and Fosphenytoin
N03AX:
|
Product |
CAS RN. |
|
Sultiame |
61-56-3 |
Phenacemide |
63-98-9 |
Lamotrigine |
84057-84-1 |
Felbamate |
25451-15-4 |
Topiramate |
97240-79-4 |
Gabapentin |
60142-96-3 |
Pheneturide |
90-49-3 |
Levetiracetam |
102767-28-2 |
Zonisamide |
68291-97-4 |
Pregabalin |
148553-50-8 |
Stiripentol |
49763-96-4 |
Lacosamide |
175481-36-4 |
Carisbamate |
194085-75-1 |
Retigabine |
150812-12-7 |
Perampanel |
380917-97-5 |
Beclamide |
501-68-8 |
APPEARANCE
IDENTIFICATION
passes Test IR, HPLC
ASSAY
98.5% min
150 ~ 154 C
LOSS ON DRYING
0.5% max
RESIDUE ON IGNITION
0.1% max
HEAVY METALS
20ppm max
WATER
0.5% max
HAZARD OVERVIEW
GHS
PICTOGRAMS
HAZARD STATEMENTS
P STATEMENTS